Configuring SED Settings
Advanced settings have reasonable defaults in place. A warning message displays for some settings advising of the dangers of making changes. Changing advanced settings can be dangerous when done incorrectly. Use caution before saving changes.
Make sure you are comfortable with ZFS, Linux, and system configuration, backup, and restoration before making any changes.
TrueNAS Enterprise
UI management of Self-Encrypting Drives (SED) is an Enterprise-licensed feature in TrueNAS 25.04 (and later). SED configuration options are not visible in the TrueNAS Community Edition. Community users wishing to implement SEDs can continue to do so using the command line sedutil-cli utility.
Managing Init/Shutdown Scripts
The Init/Shutdown Scripts widget on the System > Advanced Settings screen allows you to add scripts to run before or after initialization (start-up), or at shutdown. For example, creating a script to backup your system or run a systemd command before exiting and shutting down the system.
Init/shutdown scripts are capable of making OS-level changes and can be dangerous when done incorrectly. Use caution before creating script or command tasks.
Services
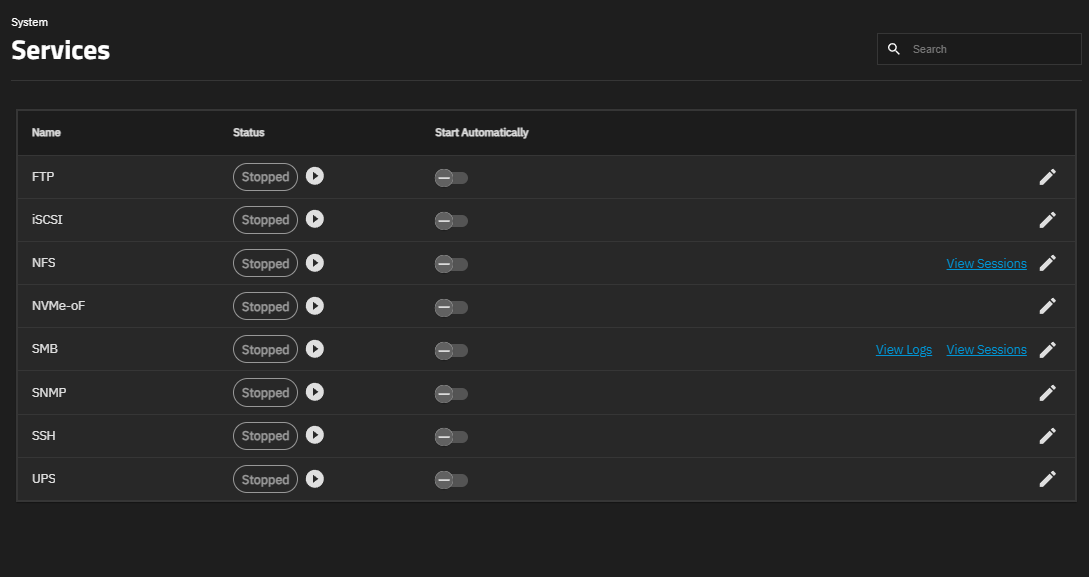
System > Services displays each system component that runs continuously in the background. These typically control data-sharing or other external access to the system. Individual services have configuration screens, activation buttons, and you can set them to run automatically.
The Configure icon opens the service configuration screen.
The NFS service row has one additional View Sessions link that opens the NFS Sessions screen.
Isolating GPU for VMs
Systems with more than one graphics processing unit (GPU) installed can isolate additional GPU device(s) from the host operating system (OS) and allocate them for use by a virtual machine (VM). Isolated GPU devices are unavailable to the OS and for allocation to applications.
Advanced settings have reasonable defaults in place. A warning message displays for some settings advising of the dangers of making changes. Changing advanced settings can be dangerous when done incorrectly. Use caution before saving changes.
Alert Settings Screen
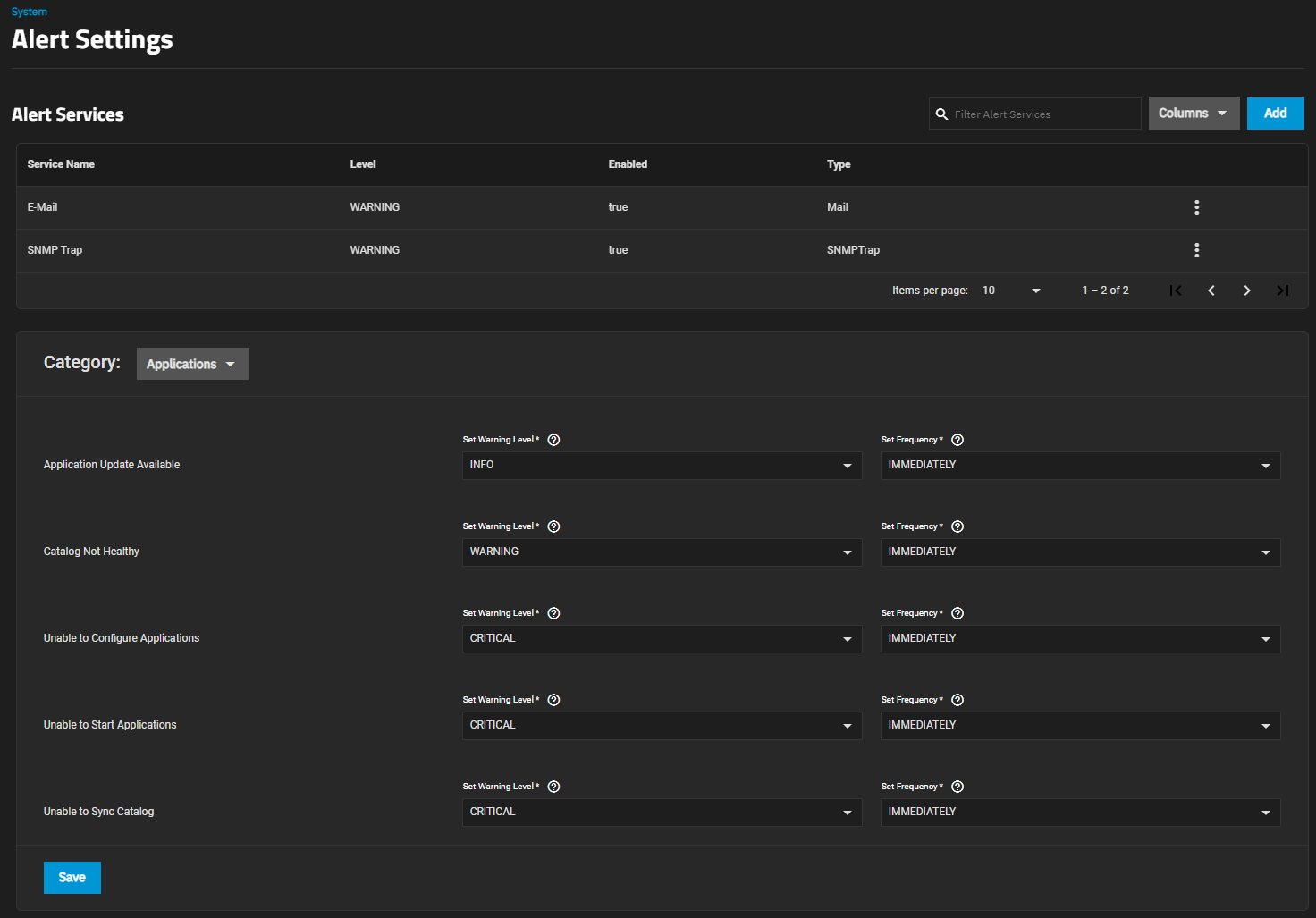
The Alert Settings screen displays options to create and edit alert services and to configure warning levels and frequencies. To access this screen, click the icon, then click the icon and select Alert Settings on the dropdown list.
Use Columns to change the information displayed in the list of alert services. Options are Unselect All, Type, Level, Enabled and Reset to Defaults.