Advanced Settings Screen
23 minute read.
Advanced settings have reasonable defaults in place. A warning message displays for some settings advising of the dangers of making changes. Changing advanced settings can be dangerous when done incorrectly. Use caution before saving changes.
Make sure you are comfortable with ZFS, Linux, and system configuration, backup, and restoration before making any changes.
The Advanced Settings screen provides configuration options for the console, syslog, audit, kernel, sysctl, storage (system dataset pool), replication, WebSocket sessions, cron jobs, init/shutdown scripts, NTP servers, allowed IP addresses, isolated GPU device(s), self-encrypting drives, and global two-factor authentication.
You can download or upload your system configuration files from this screen.
The TrueNAS UI has several fields that allow users to write custom scripts. When a user writes a password into a custom script, the password is provided in cleartext form within system debug files, creating a serious security concern.
We do not recommend using custom scripting on TrueNAS, as it is a highly advanced feature for expert storage administrators and can lead to security breaches.
TrueNAS Enterprise
Enterprise-licensed systems include configuration options for STIG and FIPS security, and failover when the system is a High Availability system.
The Manage Configuration dropdown shows two options: one to download the system config file and the other to upload a system config file. The option to reset system settings to the default configuration shows after uploading a configuration file.
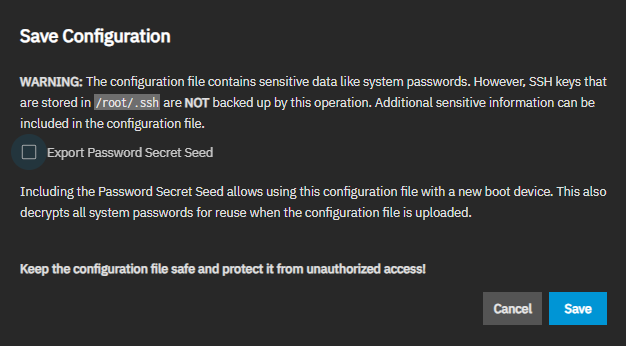
Download File opens the Save Configuration dialog, where users can download the current system configuration to their local machine.
The Export Password Secret Seed option is selected by default. It stores hashes of the passwords sufficient for authentication in the system, but does not store user passwords. The secret seed is used to decrypt encrypted fields in the TrueNAS configuration database. Various fields are encrypted because they might contain sensitive information such as cryptographic certificates, passwords (not user login passwords), or weak hashing algorithms (for example, NT hashes of SMB users). When a config file is restored without the secret seed, encrypted fields are set to empty values. This means various services can be broken due to the missing information. Examples are SMB via local accounts and apps.
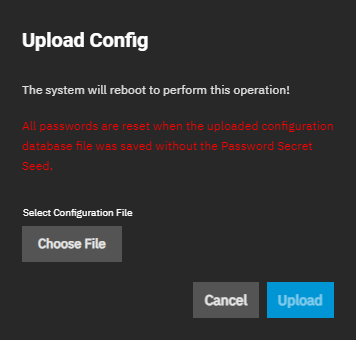
The Upload File option opens the Upload Config dialog, which allows users to choose a previously saved TrueNAS configuration to replace the current system configuration. This is useful when restoring system configuration settings after a clean install of a TrueNAS release.
Choose File opens a file browser window to locate the downloaded and saved configuration file. After selecting the file, the Upload Config window opens. Upload starts the upload of the selected configuration file.
All passwords are reset if the uploaded configuration file was saved without Export Password Secret Seed enabled.
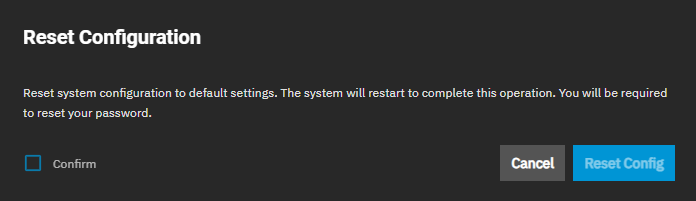
The Reset to Defaults option opens the Reset Configuration dialog. Using Resetting to Defaults returns the system configuration to factory settings and restarts the system. Users must set a new login password.
Save the current system configuration with the Download File option before resetting the configuration to default settings.
Not saving the system configuration before resetting it can result in losing data that is not backed up and losing the ability to revert to the previous configuration.
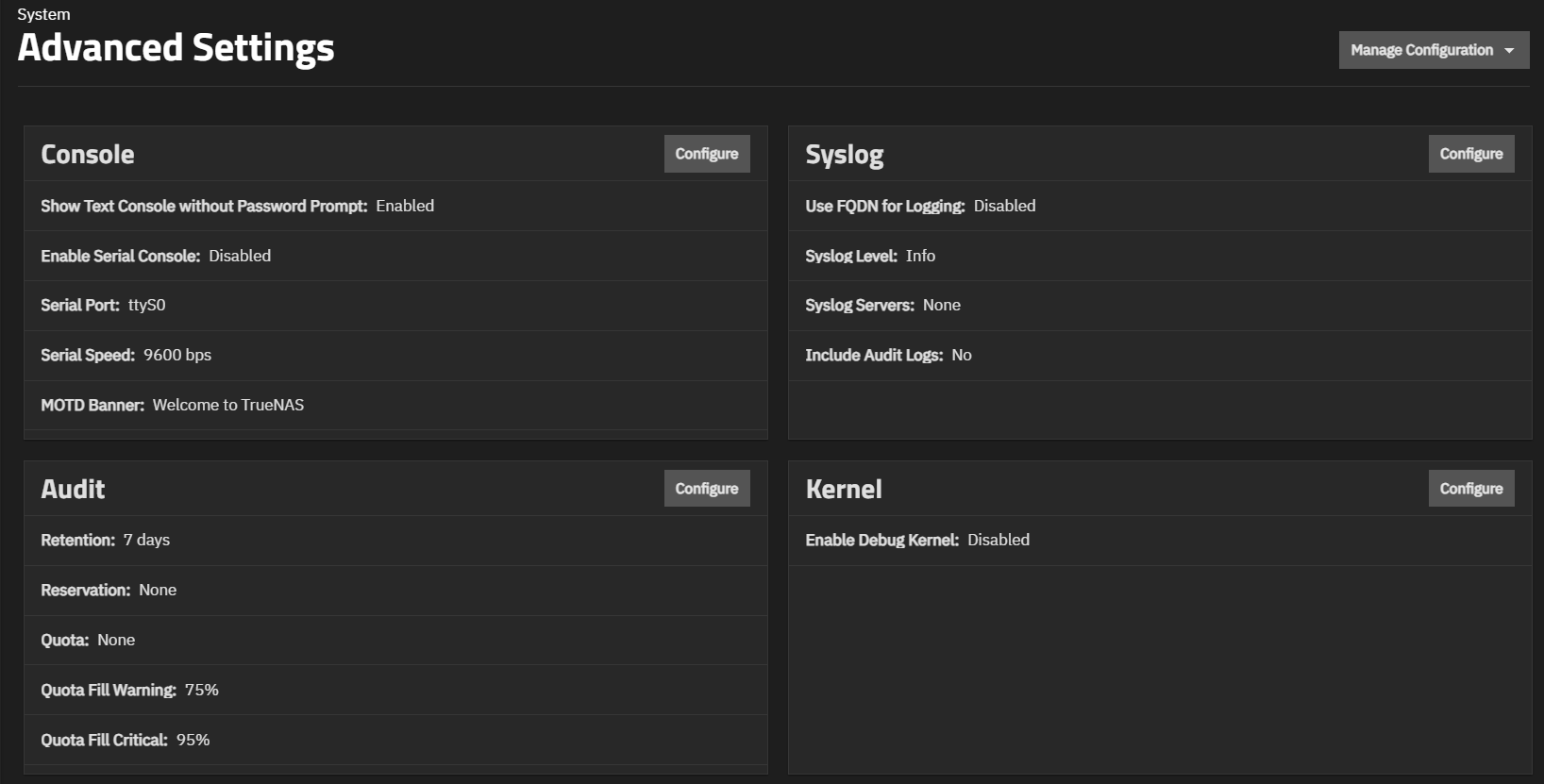
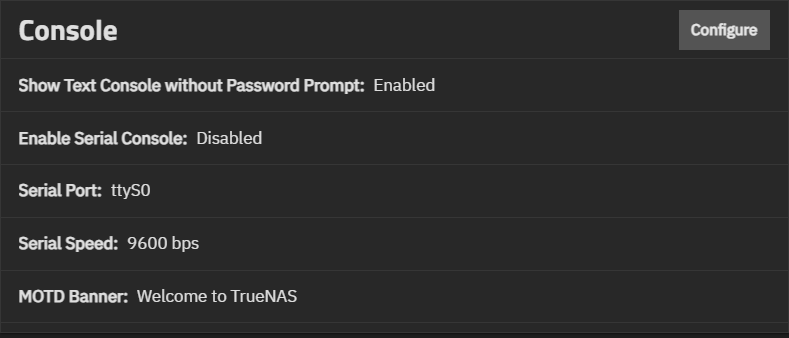
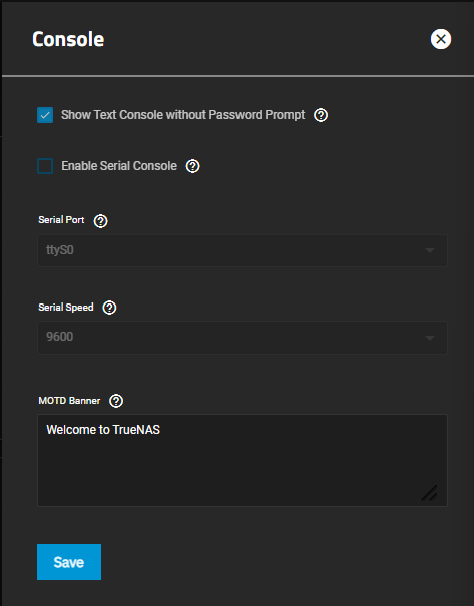
The Console widget shows the current console settings for TrueNAS, which cover setting a password prompt for the text console, enabling/disabling the serial console, the current serial port number and speed, and any banner text entered in the MOTD Banner field.
Configure opens the Console configuration screen.
Console settings configure how the Console Setup menu displays, the serial port it uses and the port speed, and the banner users see when accessing it.
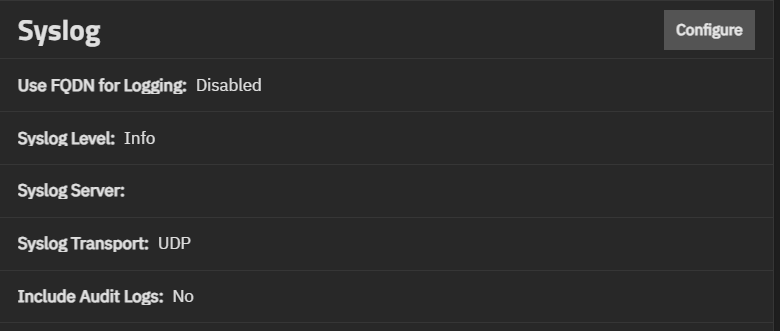
The Syslog widget displays the existing system logging settings that specify how and when the system sends log messages to system log (syslog) servers. TrueNAS allows configuring an array of two syslog servers. Each server can have its own host, transport, and TSL certificate setting.
Configure opens the Syslog configuration screen.
The Syslog settings specify the logging level the system uses to record system events to the boot device. Sets whether to use a fully qualified domain name (FQDN) for logging, and if audit logs are included. There is also an option to configure a remote syslog server for recording system events.
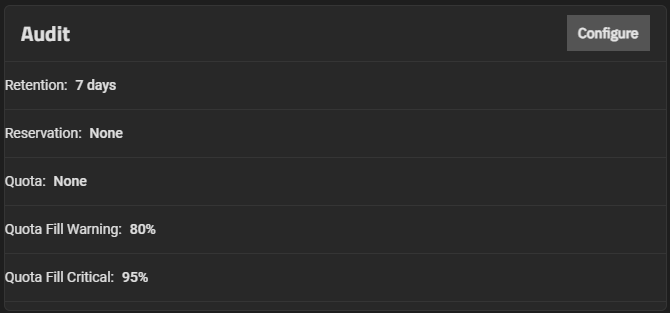
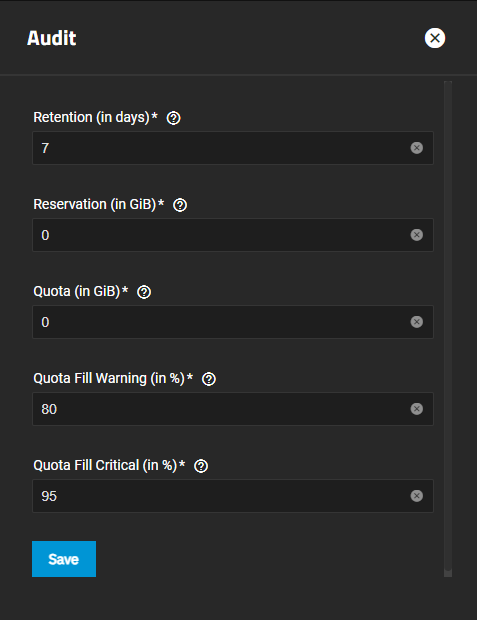
The Audit widget displays the current audit storage and retention policy settings. The public-facing TrueNAS API allows querying audit records, exporting audit reports, and configuring audit dataset settings and retention periods.
The Audit configuration screen sets the retention period, reservation size, quota size and percentage of used space in the audit dataset that triggers warning and critical alerts.
Click Configure to open the Audit configuration screen and manage storage and retention policies
The Kernel widget shows options for configuring the Linux kernel installed with TrueNAS.
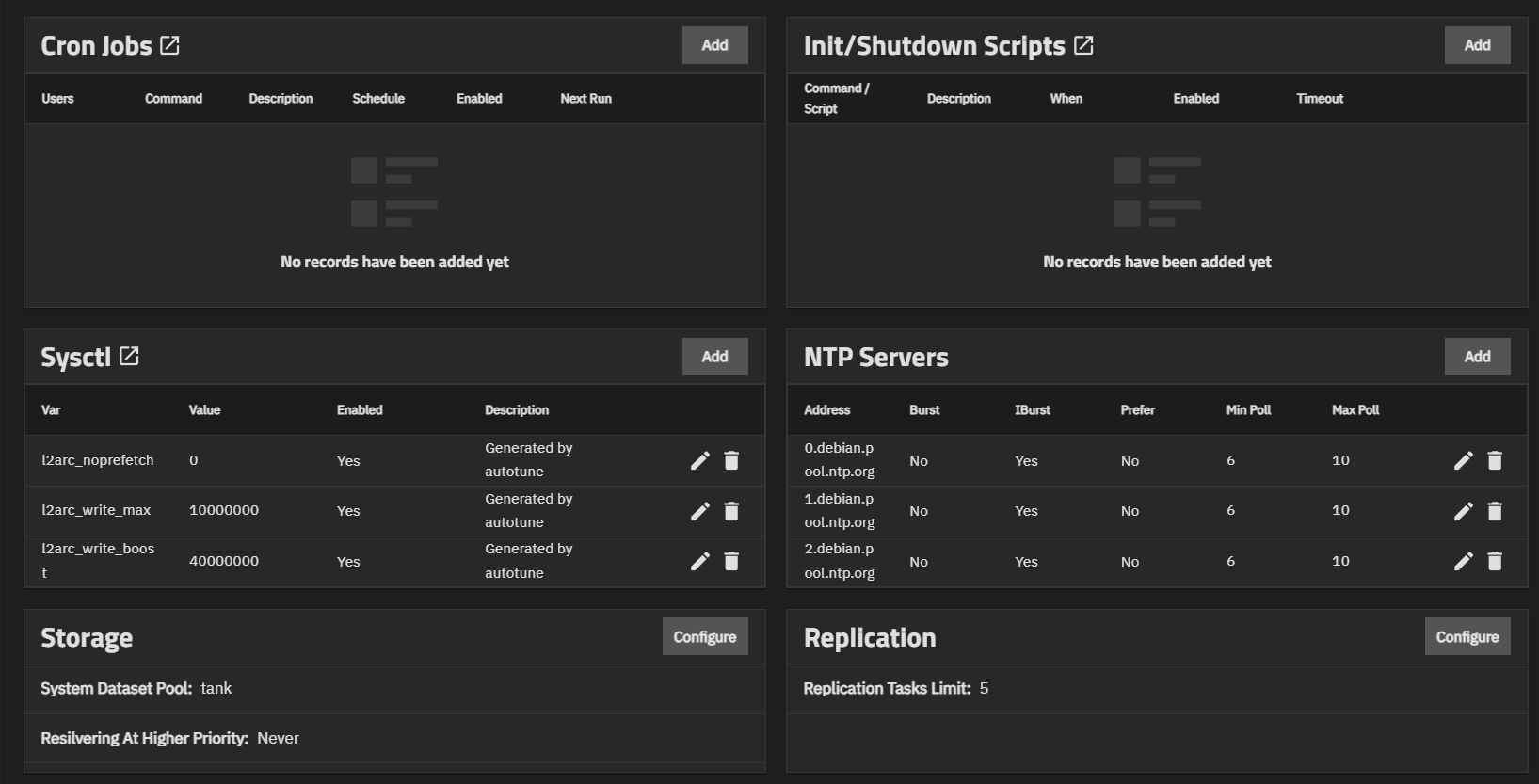
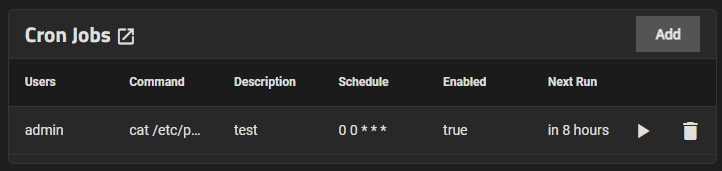
The Cron Jobs widget displays No Cron Jobs configured until you add a cron job, and then it shows the information on the cron job(s) configured on the system.
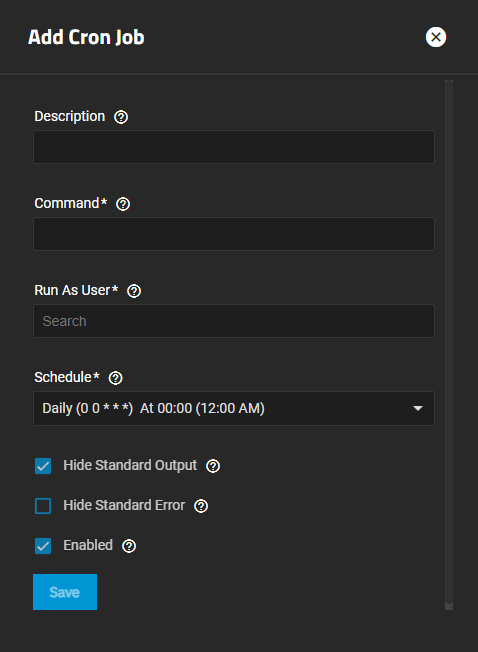
Add opens the Add Cron Job configuration screen.
Click on any job listed in the widget to open the Edit Cron Jobs configuration screen populated with the settings for that cron job.
The Add Cron Job and Edit Cron Job configuration screens display the same settings.
Cron Jobs lets users configure jobs that run specific commands or scripts on a regular schedule using cron(8). Cron jobs help users run repetitive tasks.
The Init/Shutdown Scripts widget displays No Init/Shutdown Scripts configured until you add either a command or script; then the widget lists the scripts configured on the system.
Add opens the Add Init/Shutdown Script configuration screen. Any script listed is a link that opens the Edit Init/Shutdown Script configuration screen populated with the settings for that script.
Init/Shutdown Scripts lets users schedule commands or scripts to run at system startup or shutdown.
The Sysctl widget displays either No Sysctl configured or the existing sysctl settings on the system.
Add to add a tunable that configures a kernel module parameter at runtime.
The Add Sysctl or Edit Sysctl configuration screen settings let users set up tunables to configure kernel parameters at runtime.
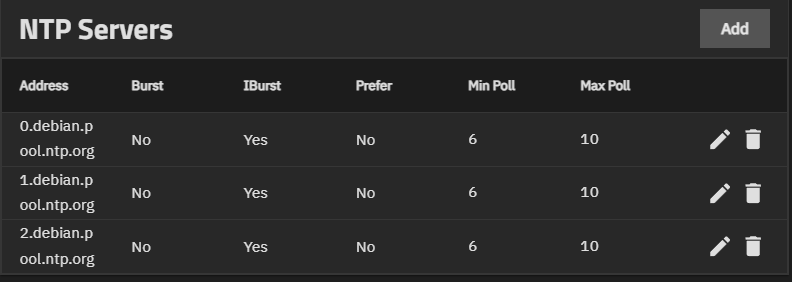
The NTP Servers widget allows users to add Network Time Protocol (NTP) servers. These sync the local system time with an accurate external reference. By default, new installations use several existing NTP servers. TrueNAS supports adding custom NTP servers.
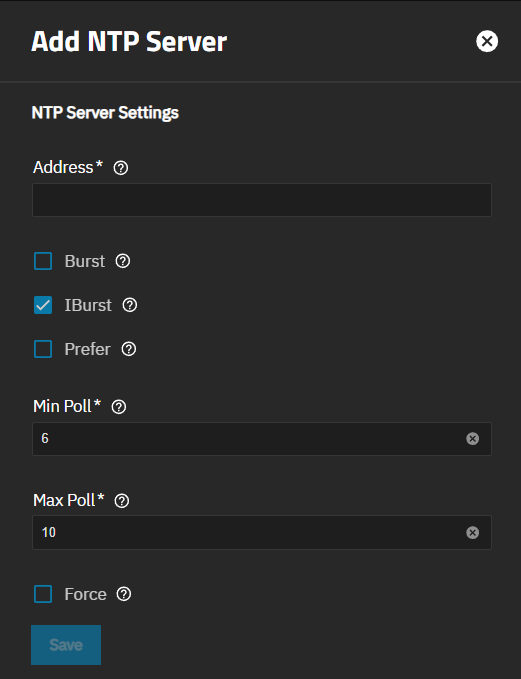
The Add NTP Server screen shows Network Time Protocol (NTP) server settings that sync the local TrueNAS system with an accurate external reference. By default, new installations use several existing NTP servers. TrueNAS supports adding custom NTP servers.
Add on the NTP Servers widget opens the Add NTP Server screen.
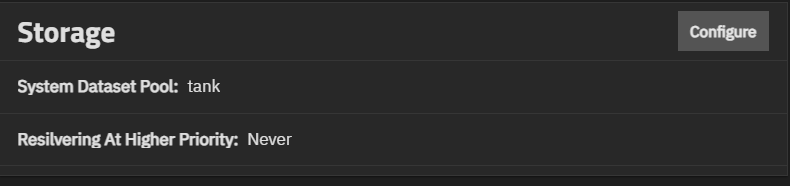
Storage widget shows the pool configured as the system dataset pool, and allows users to select the storage pool they want to hold the system dataset. The system dataset stores core files for debugging and keys for encrypted pools. It also stores Samba4 metadata, such as the user and group cache and share-level permissions.
It also shows the resilivering priority setting.
Configure opens the Storage Settings configuration screen.
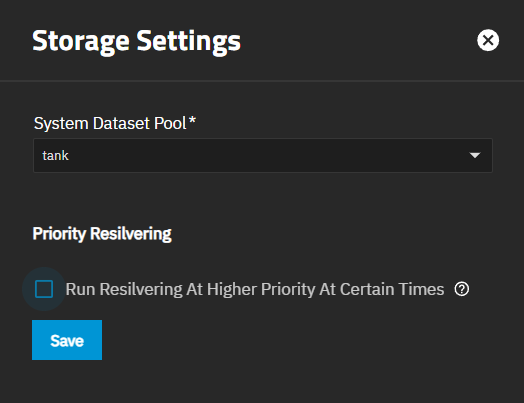
The Storage Settings screen shows the current system dataset and resilvering priority.
System Dataset Pool shows all pool root datasets configured in the system. If the system has one pool, TrueNAS configures that pool as the system dataset pool. If your system has more than one pool, you can set the system dataset pool using the Select Pool dropdown. Users can move the system dataset to an unencrypted pool or an encrypted pool without passphrases. Users can move the system dataset to a key-encrypted pool, but cannot change the pool encryption type afterward. You cannot move the system dataset to an encrypted pool with a passphrase set.
Run Reslivering At Higher Priority At Certain Times is not enabled by default. Selecting this option shows additional fields to set the time and date to resliver the system dataset pool disks.
Days of the Week shows a dropdown list of day options. From and To set the time range in which a resliver can run.
Save implements setting changes.
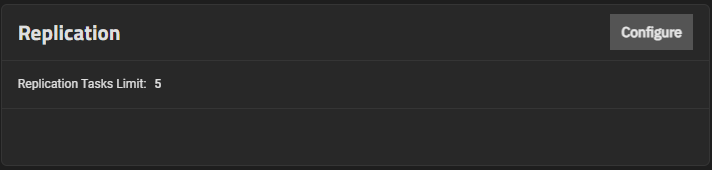
The Replication widget displays the number of replication tasks that can execute simultaneously on the system. It allows users to adjust the maximum number of replication tasks the system can perform simultaneously.
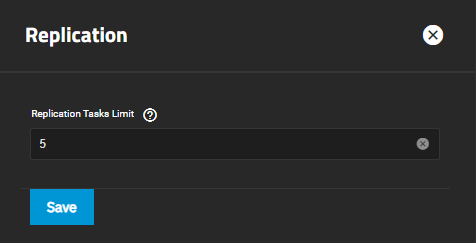
Click Configure to open the Replication configuration screen.
Enter a number for the maximum number of simultaneous replication tasks you want to allow the system to process and click Save.
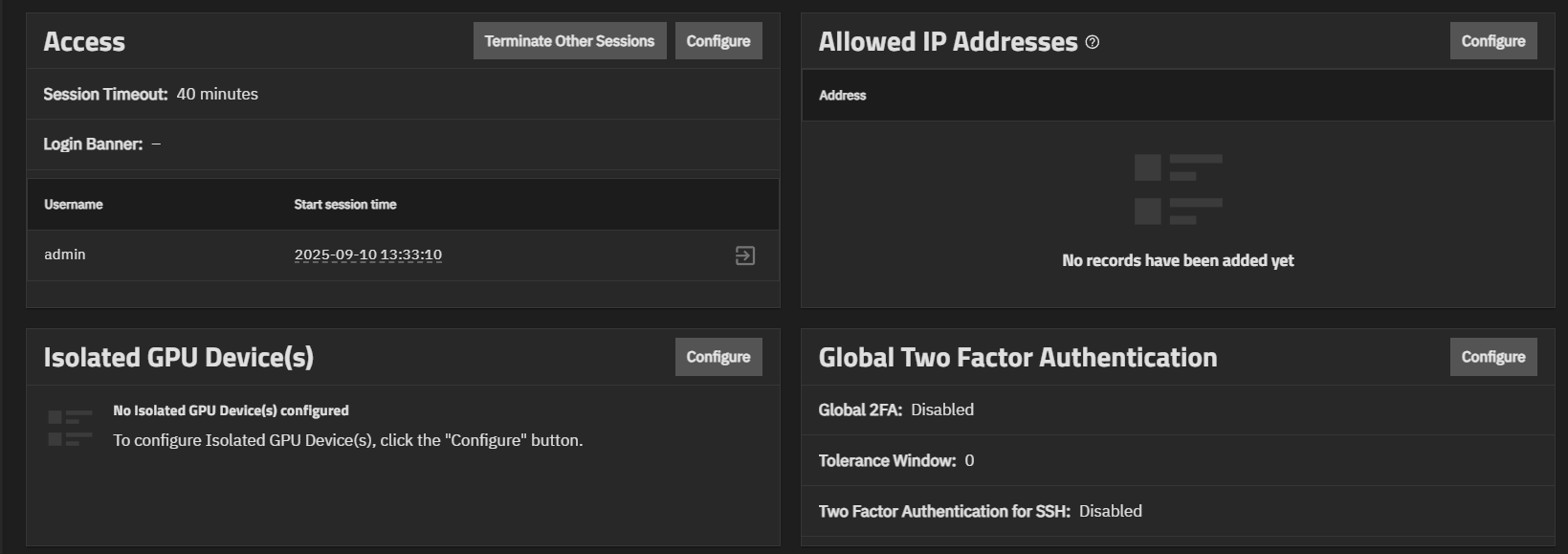
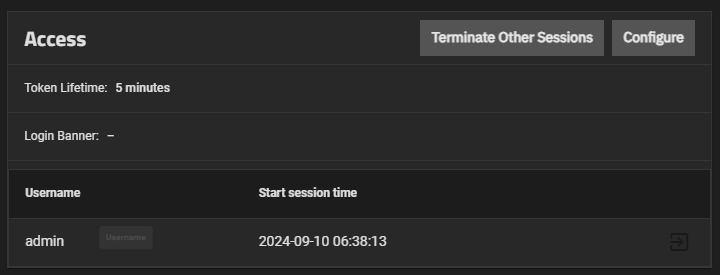
The Access widget shows a list of all active sessions including the current logged-in user and the time it started. The Session Timeout setting shows the number of minutes for the current session.
The Login Banner shows the custom text entered on the Access Settings screen. This text shows before the login screen. When configured, users see the login banner and must click Continue to show the TrueNAS login splash screen.
Administrators can manage other active sessions and configure the session timeout for their accounts.
Terminate Other Sessions ends all sessions except the current session. To end individual sessions, click the logout button next to that session. You must check a confirmation box before the system allows you to end sessions.
The logout icon is inactive for the currently logged-in administrator session and active for any other current sessions. It cannot be used to terminate the currently logged-in active administrator session.
Session Timeout shows the configured token duration for the current session (default is five minutes). TrueNAS logs out user sessions that are inactive for longer than the configured token setting for the user. New activity resets the token counter.
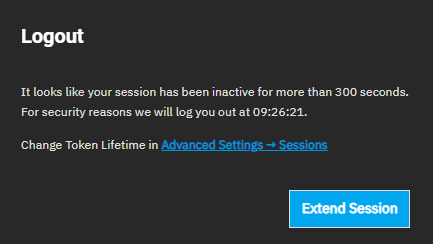
When the configured session timeout is exceeded, TrueNAS displays a Logout dialog with the exceeded ticket lifetime value and the time the session is scheduled to terminate.
Click Extend Session to reset the token counter. If not clicked, TrueNAS terminates the session automatically and returns to the login screen.
To change settings, click Configure to open the Access Settings screen, where you can configure a session timeout or add a login banner.
If the configured session timeout is exceeded, TrueNAS displays a Logout dialog with the exceeded ticket lifetime value and the time the session is scheduled to terminate.
Configure opens the Access Settings screen.
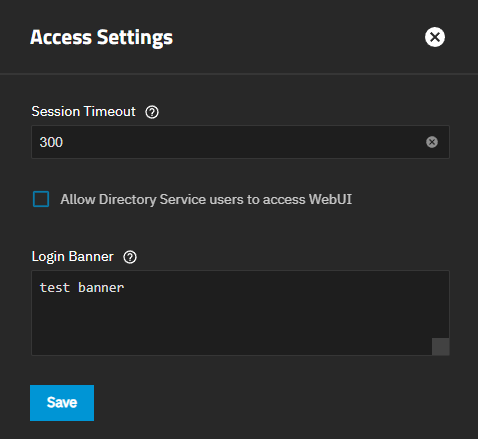
The Access Settings screen allows users to configure the Session Timeout for the current account.
Select a value that fits your needs and security requirements. Enter the value in seconds.
The default lifetime setting is 300 seconds or five minutes.
The maximum is 2147482 seconds or converting it to hours/minutes/seconds, 596 hours, 31 minutes, and 22 seconds. If converting it to days/hours/minutes/seconds, 24 days, 20 hours, 31 minutes, and 22 seconds.
The Login Banner field allows specifying a text message that the system shows before the TrueNAS login splash screen displays. Continue on the banner screen closes the screen, then shows the login splash screen. The maximum length of the banner text is 4096 characters, including spaces. Long text wraps and banner text can use carriage returns to break up long messages to improve readability. Leave Login Banner empty to show just the login screen without interruption by a banner screen.
TrueNAS Enterprise
Enterprise-licensed systems include the Allow Directory Service users to access WebUI option on the Access Settings screen. After enabling this option, TrueNAS automatically creates a new entry, named as the domain admin group, in the Privileges screen table. For example, if the domain is ad03.mydomain.net, then you should see a group of that name listed as well as any of the groups AD creates on the system.
The Allowed IP Addresses widget displays IP addresses and networks added to the system that are allowed to use the API and UI. If this list is empty, then all IP addresses are allowed to use the API and UI.
Configure opens the Allowed IP Addresses configuration screen.
Entering an IP address into the allowed IP address list denies access to the UI or API for all other IP addresses not listed.
Only use when limiting system access to a single or a limited number of IP addresses. Leave the list blank to allow all IP addresses.
Add, next to Allowed IP Addresses, adds an entry to the allowed IP Addresses list. Ensure the first address and/or subnet includes your current client system.
Enter a specific IP address, for example, 192.168.1.1, for individual access, or use an IP address with a subnet mask, like 192.168.1.0/24, to define a range of addresses.
You can add as many addresses as needed.
Save retains setting changes and closes the screen.. A Restart Web Service dialog opens. Confirm activates Continue. and Continue restarts the web UI and applies changes.
TrueNAS Enterprise
UI management of Self-Encrypting Drives (SED) is an Enterprise-licensed feature in TrueNAS 25.04 (and later). SED configuration options are not visible in the TrueNAS Community Edition. Community users wishing to implement SEDs can continue to do so using the command line sedutil-cli utility.
Note: Additional changes to SED management options in the TrueNAS UI ahead of the 25.04.0 release version, with documentation updates to follow.
The Self-Encrypting Drive (SED) widget shows when the system has self-encrypting drives, and shows the system ATA security user and password.
Configure opens the Self-Encrypting Drive configuration screen.
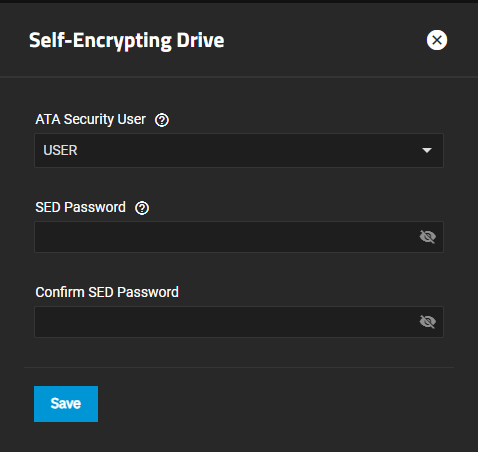
The Self-Encrypting Drive configuration screen allows users to set the ATA security user and create a SED global password.
The Isolated GPU Device(s) widget displays any isolated graphics processing unit (GPU) device(s) configured on your system.
Configure opens the Isolated GPU PCI Ids screen, which allows users to isolate additional GPU devices.
The Isolate GPU PCI IDs widget shows GPU devices added in TrueNAS. Configure opens the configuration screen and allows you to isolate GPU devices for a virtual machine (VM).
To isolate a GPU, you must have at least two in your system; one allocated to the host system for system functions and/or applications, and the other available to isolate for use by a VM.
Select the GPU device ID from the dropdown list and click Save.
Isolated GPU devices are reserved for use by configured applications or a VM.
To allocate an isolated GPU device, select it while creating or editing the VM configuration. When allocated to a VM, the isolated GPU connects to the VM as if it were physically installed in that VM, and it becomes unavailable for any other allocations.
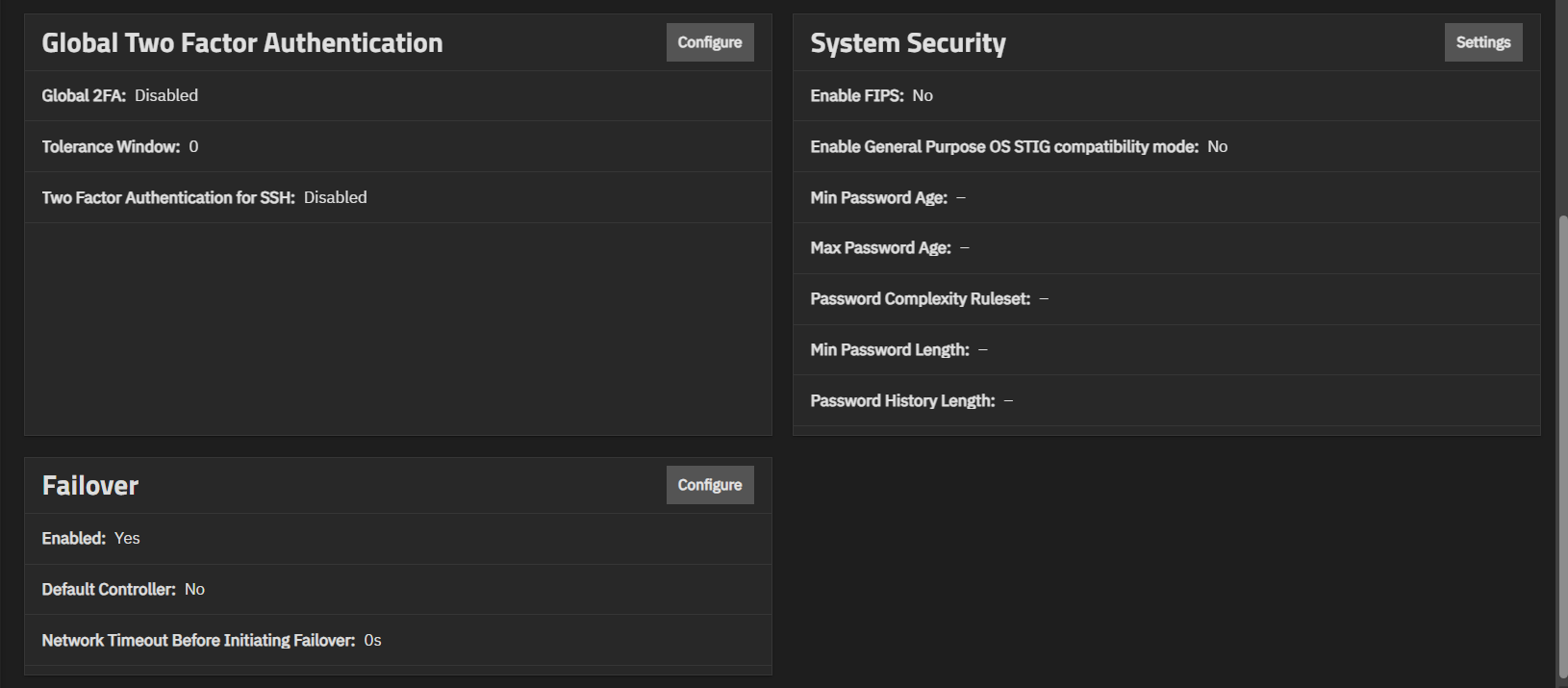
The Global Two Factor Authentication widget shows the status of global two-factor authentication, the tolerance window, and the status of two-factor authentication for SSH sessions. It provides access to the configuration screen that allows you to set up two-factor authentication (2FA) for your system.
The widget displays the following information:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Global 2FA | Shows whether Global 2FA is enabled or disabled. |
| Tolerance Window | Shows the current tolerance window value. |
| Two Factor Authentication for SSH | Shows whether 2FA for SSH is enabled or disabled. |
Configure opens the Global Two Factor Authentication configuration screen.
TrueNAS Enterprise
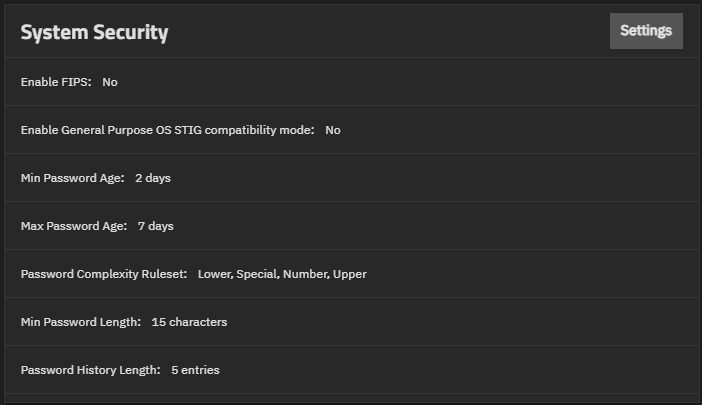
The System Security widget allows administrators of Enterprise-licensed systems to enable or disable FIPS 140-2 compliant algorithms, general-purpose OS STIG compliance, and other administrator account rules. Changing FIPS or STIG settings requires a system restart to apply the setting changes.
High Availability (HA) systems restart the standby controller and then show a prompt to failover and restart the primary controller.
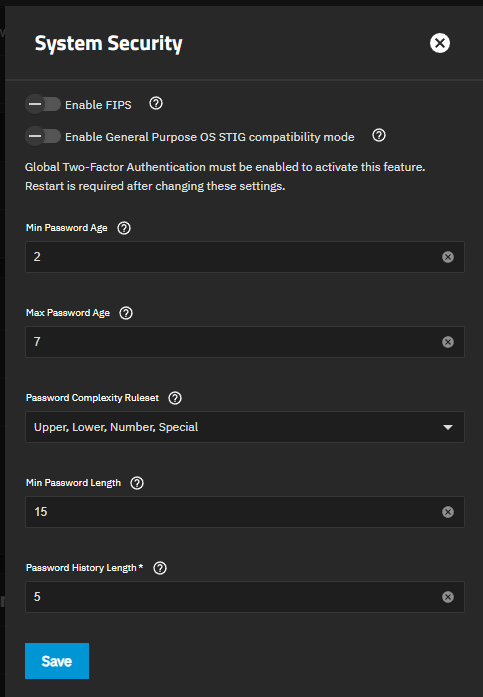
Settings opens the System Security configuration screen.
The Enable FIPS toggle enables or disables enforcement. The Enable General Purpose OS STIG compatibility mode toggle enables or disables the STIG compliance implementation. Requires two-factor authentication for an admin user with full permissions before enabling STIG compatibility.
Administrator Password settings
Name Description Min Password Age Minimum number of days a password must be used before it can be changed. Max Password Age Maximum number of days a password can be used before it must be changed. TrueNAS warns users of password expiration seven days prior to the set expiration date. Password Complexity Ruleset Defines the required character types for administrator passwords. Choose between Upper, Lower, Number, and Special character type requirements. Min Password Length Define how many characters must be present in an administrator password. The default required minimum is 8 characters. Password History Length Define how many previously used passwords to remember. Prevents administrators from reusing passwords when updating credentials. Requires an integer between 1 and 10.
TrueNAS Enterprise
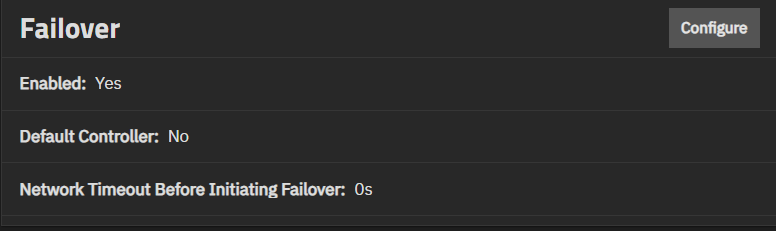
The Failover widget shows only on Enterprise-licensed HA systems. It shows the status of failover, the default controller, and the network timeout before TrueNAS initiates failover.
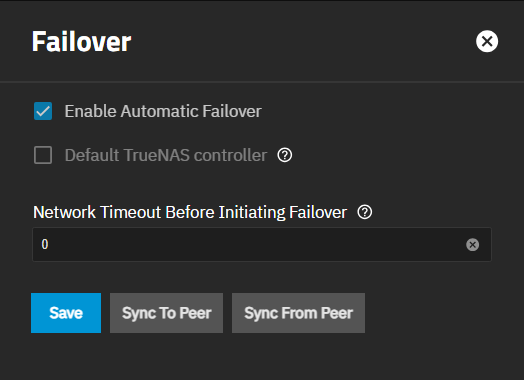
Configure opens the Failover configuration screen.
The Failover screen shows settings used on TrueNAS Enterprise (HA) systems to turn the failover function on or off, sync the primary and standby controllers, and allow administrator users to configure failover. The main menu option and screen only display on Enterprise (HA) systems with the correct license applied.
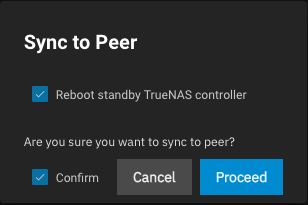
Setting Description Enable Automatic Failover Set the system to turn on failover. Leave clear to disable failover. Default TrueNAS controller Sets the current active controller to be the default controller when both TrueNAS controllers are online and HA is enabled. To change the default TrueNAS controller, leave unselected on the default TrueNAS controller and allow the system to fail over. This process briefly interrupts system services. Network Timeout Before Initiating Failover Sets the number in seconds to wait after a network failure before triggering a failover. The default value is 0, which means failover occurs immediately or after two seconds when the system is using a link aggregate. Sync To Peer Initiates a sync operation that copies over the primary controller configuration to the standby controller. Opens the Sync To Peer dialog to confirm the operation. Sync From Peer Initiates a sync operation that copies over the standby controller configuration to the primary controller. Sync To Peer and Sync From Peer buttons each open a confirmation dialog before TrueNAS performs the operation requested.
Setting Description Reboot standby TrueNAS controller Select to cause the standby controller to restart after the sync operation completes. Confirm Select to confirm you want to perform the sync-to-peer operation. Proceed Begins the sync operation.