Datasets
23 minute read.
The Datasets screen and widgets show information about datasets and zvols, provide access to data management functions, indicate the dataset roles, list the services using the dataset, show encryption status, and list permissions for datasets. The screen focuses on managing data storage, including user and group quotas, snapshots, and other data protection measures.
The Datasets screen shows No Datasets and a Create Pool button until you add a pool and the first root dataset.
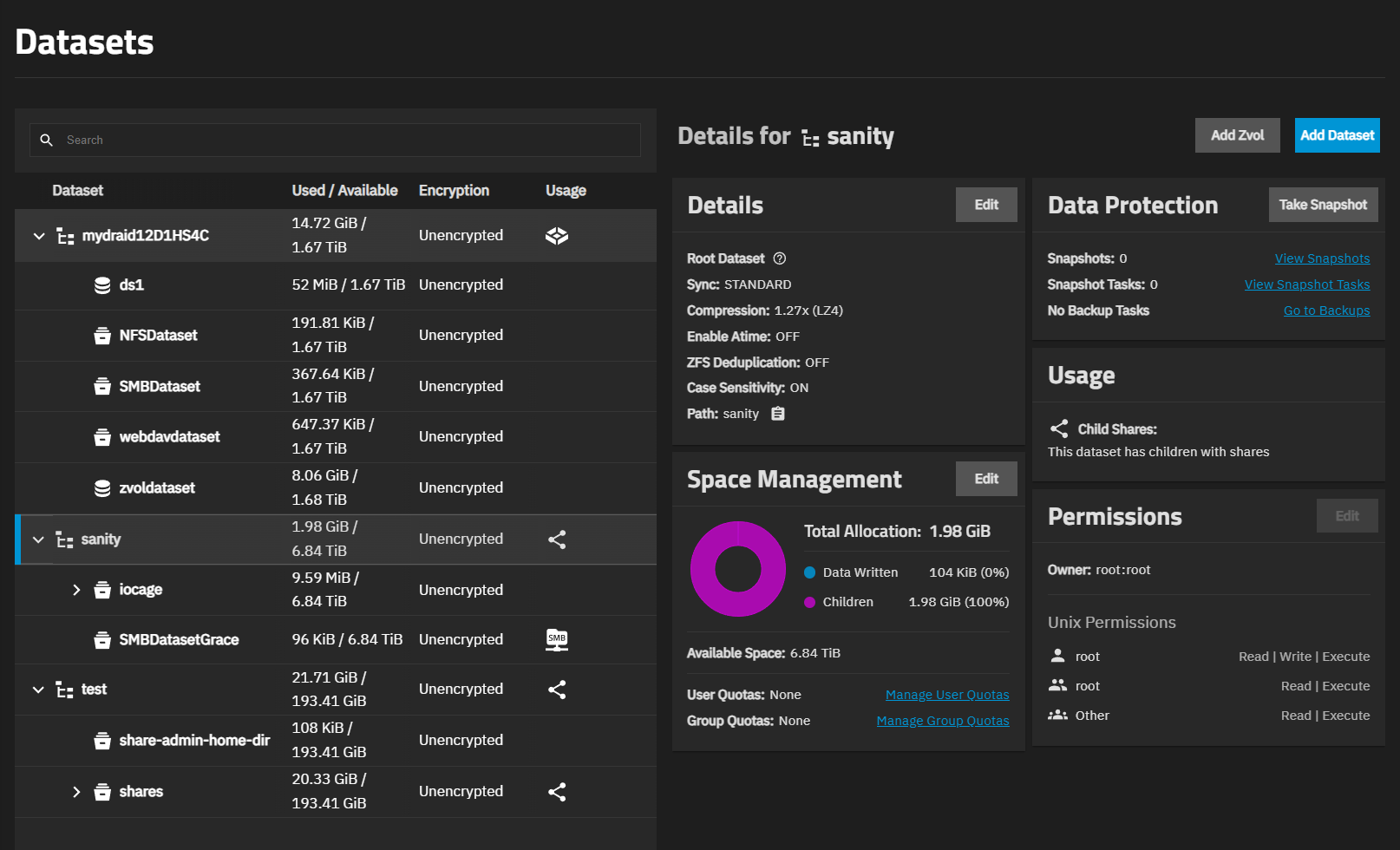
After creating a dataset, the screen shows the dataset tree table on the left and the Details for datasetname dataset widgets on the right. The tree table with multiple datasets lists parent and child datasets (or zvols) on the system. Icons representing the storage type or a service, such as SMB share or the system dataset, show at the right of a row.
Large petabyte systems might report storage numbers inaccurately. Storage configurations with more than 9,007,199,254,740,992 bytes round to the last 4 digits. For example, a system with 18,446,744,073,709,551,615 bytes reports the number as 18,446,744,073,709,552,000 bytes.
Add Zvol opens the Add Zvol screen.
Add Dataset opens the Add Dataset screen.
Begin typing the name of a dataset in the Search field to filter datasets to a short list of those matching what is typed.
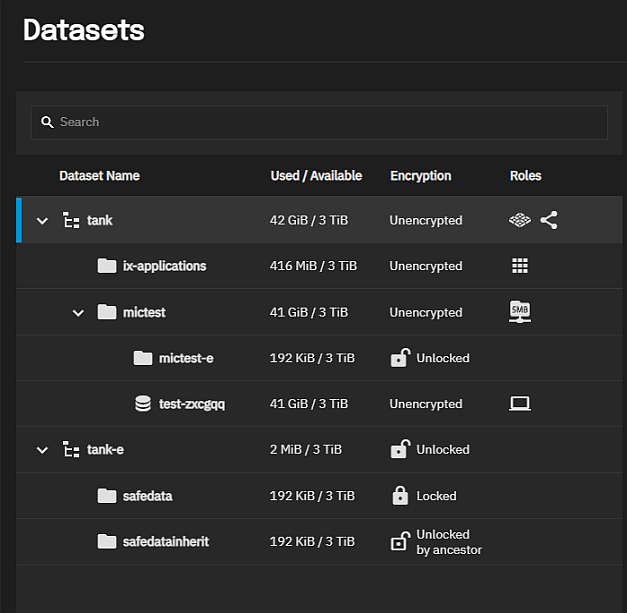
The datasets tree table shows an expandable hierarchical structure, starting with the root dataset, then each non-parent or parent and child datasets, with the child datasets nested under each parent dataset.
The top row of the tree table is selected by default when you go to the Datasets screen. The widgets on the right show information for the selected dataset.
Click on any parent dataset to expand the tree table to show nested child datasets.
The table of datasets shows used and available storage space for each dataset, encryption status (locked, unlocked, or unencrypted), and dataset usage, such as the services using it (e.g., the system dataset, a share, virtual machine, or application). Datasets and zvols have different icons.
The
The
Each dataset has a set of information cards (widgets) in the Details for datasetname area of the screen. These widgets and information is grouped by functional areas. The widgets for a root or parent dataset differ from a child dataset, or a dataset used by another service or with encryption.
Dataset widgets are:
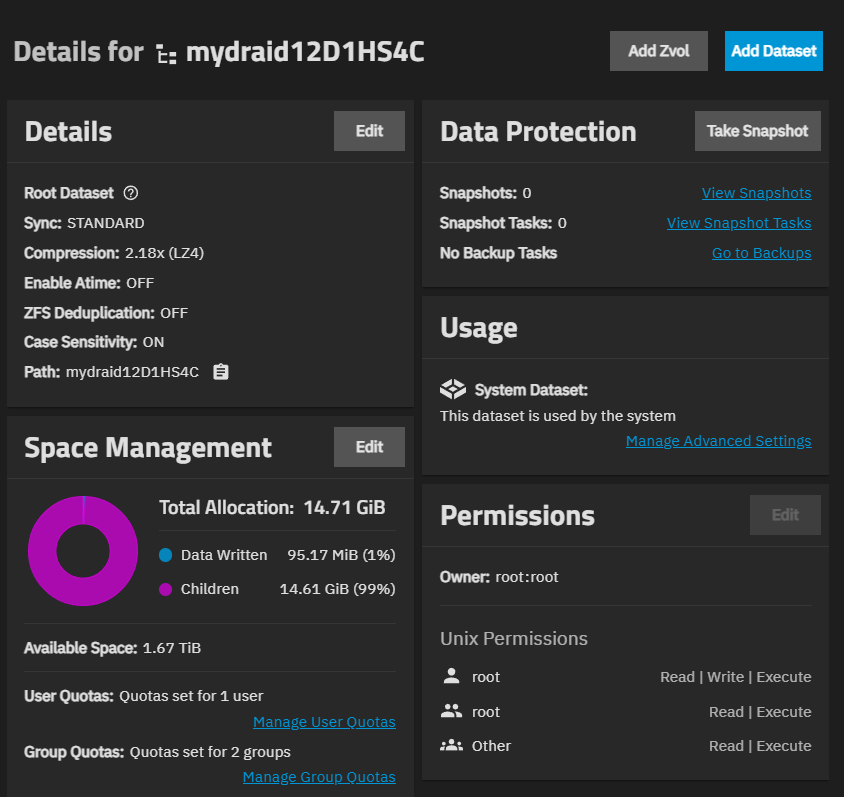
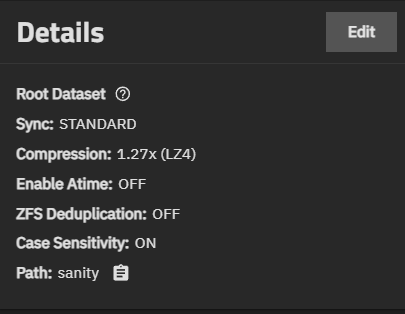
The Details widget shows information about the dataset that allows you to manage an existing dataset.
Information includes:
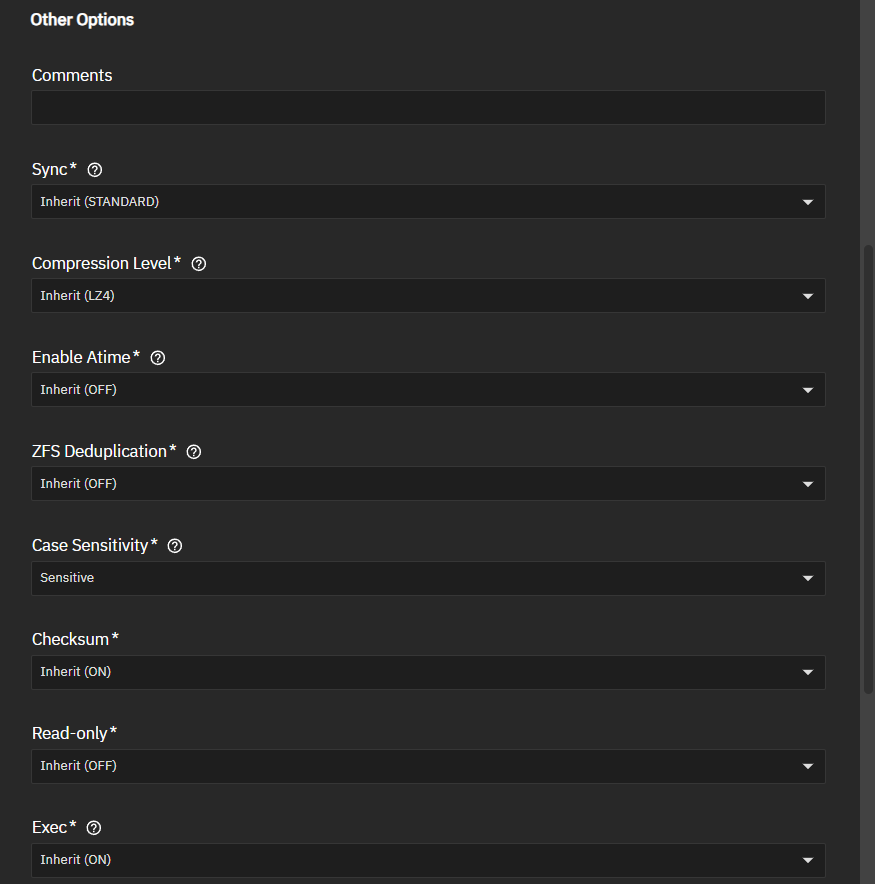
- Sync - Shows the type of dataset. For example, STANDARD for non-root datasets or ROOT DATASET for the first pool or root dataset, which is usually the system dataset.
- Compression - Shows the compression algorithm applied to the dataset. See Data Compression Algorithms for more information.
- Enable Atime - Shows if this is on or off. See Advanced Options for more information.
- ZFS Deduplication - Shows if ZFS deduplication is on or off. See Advanced Options for more information.
- Case Sensitivity - Shows if case sensitivity is on or off. See Advanced Options for more information.
- Path - Shows the mount path to the dataset.
A root dataset path shows the pool name alone. If there are multiple pools on the system, the first pool created is the system dataset. The root dataset for a pool is the top-level container in your pool, sharing the same name as the pool itself. When managing your TrueNAS system, it is generally best practice to create dedicated datasets under the root dataset for different types of data, rather than storing data directly in the root dataset itself.
Edit opens the Edit Dataset screen for the selected dataset.
Delete shows on the Details widget for non-root datasets. Use the Disconnect/Export option on the Storage Dashboard screen to deleate a root dataset.
Delete opens a Delete dataset window with information about other options or services using the dataset, for example, a parent to other datasets, the services child datasets of a parent dataset uses, shares like SMB and/or NFS, or a multiprotocol share, and the path to the datasets the shares use.
Promote shows on the Details widget for a dataset created by cloning a snapshot on the dataset tree table. It promotes the cloned child dataset and allows users to delete the parent volume that created the clone. Otherwise, you cannot delete a clone while the original volume still exists. See zfs-promote.8.
The Delete window shows information about the dataset, including the path, services that depend on the dataset, and shares using the dataset and the path to the dataset.
If a service does not use a dataset, the Delete window does not show a service.
The window includes a field where you enter the path to the dataset. Confirm activate the Delete Dataset button. Delete Dataset deletes the dataset and all data it contains.
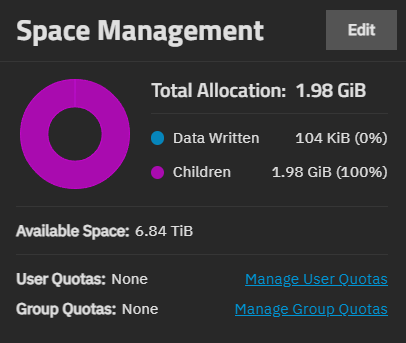
The Space Management widget shows the total space allocation (data written, children of the dataset, available space). The widget shows if an encrypted dataset is unlocked. After locking the dataset, this widget disappears until you unlock the dataset.
The donut graph on the widget provides at-a-glance information and numeric values for the space allocated and used in the selected dataset. This includes data written and space allocated to child datasets of this dataset. It shows the available space in the dataset.
Manage User Quota opens the User Quotas screen. Manage Group Quotas opens the Group Quotas screen.
Edit opens the Capacity Settings screen where you can set quotas for the dataset.
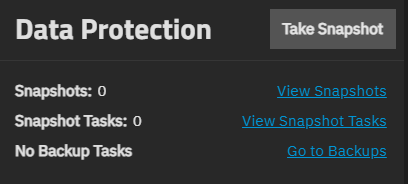
The Data Protection widget shows snapshot and backup task information for the dataset.
Take Snapshot opens the Add Snapshot screen.
View Snapshot Tasks opens the Data Protection screen where you can add or manage scheduled periodic snapshot tasks.
No Backup Tasks shows when no data protection backup tasks are created. Go to Backups opens the Data Protection screen, where you can manage scheduled replication, rsync, and other data protection tasks.
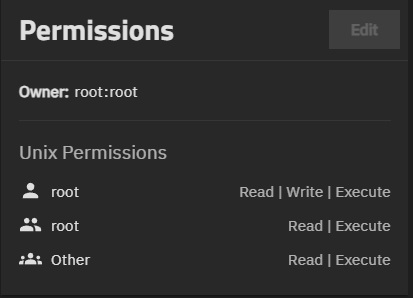
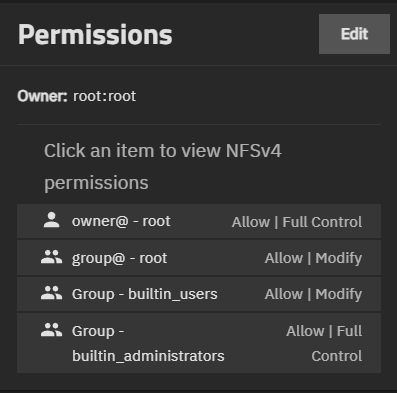
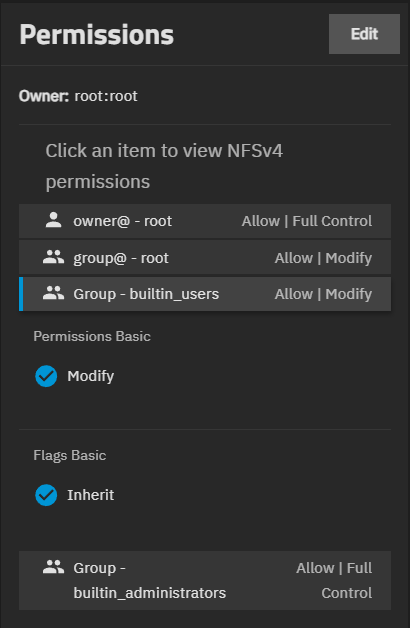
The Permissions widget shows the type of ACL permissions applied to the dataset. ACL types can be NFSv4 or Unix Permissions (POSIX), and each lists access control user or group entries, and the owner and group for the dataset.
The widget shows the owner and type of access control list (ACL) and ACL Entries (ACEs) for the dataset in the lower portion of the widget. Owner shows both the onwer user and group on one line, formatted as owner:group. For example, Owner: root:root.
The permission screen and widget options vary based on the ACL type. Root datasets have POSIX permissions, and the entries are not editable.
Non-root dataset can be POSIX or NFSv4 based on the Dataset Preset selected when you create the dataset.
NFSv4 ACL type (the default ACL type) shows the user and group entries on the Permissions widget as buttons that show selectable options to change selectable Permissions Advanced and Flags Advanced options for that entry on the Permissions widget.
Edit for a POSIX ACL opens the Unix Permissions Editor screen. Root datasets do not show the Edit button.
Edit for an NFSv4 ACL opens the Edit ACL screen.
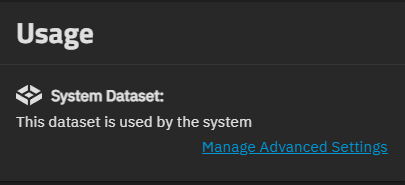
The Usage widget shows the dataset role or services that use it (i.e., a share, application, virtual machine, or the system dataset). It shows an icon for and information about the service using the dataset. A corresponding icon shows on the row for the dataset in the dataset tree table.
The Manage Advanced Settings shows for the system dataset, and opens the Advanced Settings screen. If the dataset is associated with a share, a Manage SMB Share link shows. where SMB is the share type and opens the corresponding share screen.
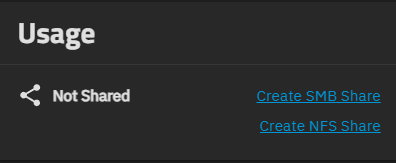
It shows Not Shared if the dataset is configured with a share preset like SMB but does not have a share created. The Usage widget shows two links: Create SMB Share that opens the Add SMB screen and Create NFS Share that opens the Add NFS screen.
The Usage widget for a parent dataset with child datasets with shares shows this, but does not link to other screens.
| Usage | Link Included | Description |
|---|---|---|
| System dataset | Manage Advanced Settings | Select the option to configure the System Dataset |
| Apps | Manage Apps Settings | Shows the app using the dataset. |
| Dataset with no share | Create SMB Share Create NFS Share | Opens either the Add SMB or Add NFS share screen to configure the share. |
| SMB share | Manage SMB Shares | Shows the name of the SMB share using the dataset. Select the snare on the Sharing SMB screen to edit it. |
| Other share | Link to the share type screen | Shows the name of the share using the dataset. Select the option on the share screen (NFS or iSCSI) to edit it. |
| Multiprotocol share | Manage SMB Shares Manage NFS Shares | Shows the name of the SMB and NFS share using the dataset. Each link opens the Sharing SMB or Sharing NFS screens. Click on the share to edit it. |
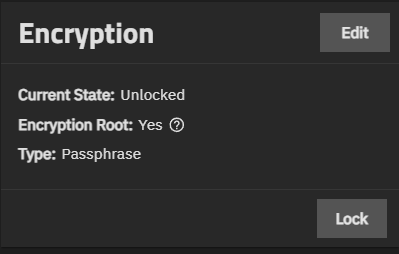
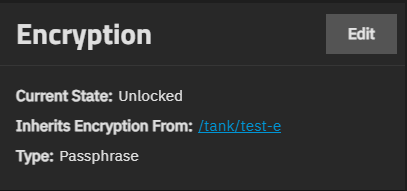
The Encryption widget only shows for encrypted datasets. Options shown in the widget vary based on the type of dataset (root, non-root parent, or child dataset), and whether the dataset is a encrypted parent or an encrypted child dataset that inherits settings from the parent. It includes the current state of the dataset encryption, the encryption root, and the type.
The Encryption widget shows Lock when the dataset is unlocked or Unlock when the dataset is locked. These are not available on the widget for the root dataset. The dataset table also shows Locked or Unlocked by Parent.
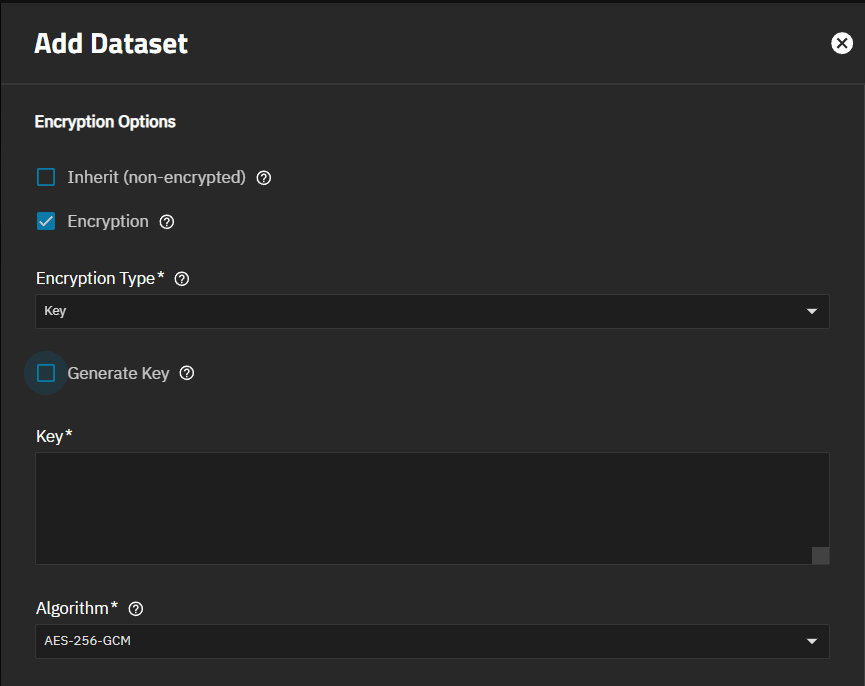
The Encryption widget shows Export Key when the encryption type is set to key. Export Key downloads the system-generated encryption key to a JSON file. You can find this in your Windows Downloads folder.
Edit opens the Edit Encryption Options for datasetname window. A root dataset does not include the Edit button. We do not recommend encrypting the root or system dataset!
For more details on encryption windows and functions, see Encryption Settings.
The Add Dataset and Edit Dataset screens allow admin users with full control access to create and manage datasets. Both screens include the same Advanced Options settings but you cannot change the dataset name, Dataset Preset selection, or the Case Sensitivity settings on the Advanced Options screen after clicking Save on the Add Dataset screen.
Edit on the Dataset Details widget opens the Edit Dataset screen.
Edit on the Encryption widget opens an encryption edit window. The Encryption widget only shows if a dataset is encrypted. Edit on the Permissions widget opens the Edit ACL screen to edit dataset NFSv4 permissions. POSIX ACLs open the Unix Permissions Editor screen.
Add Dataset and Edit Dataset screens include the Basic Options and Advanced Options. TheBasic Options and Advanced Options screens shows the Name and Options section.
The Advanced Options screen shows:
- Quota management tools and settings
- Encryption Options settings
- Other Options settings
The Basic Options show on the Advanced Options screen.
The Add Dataset and Edit Dataset screens show the Advanced Options button. Advanced Options show:
- Quota Management settings
- Encryption settings
- Other Options settings
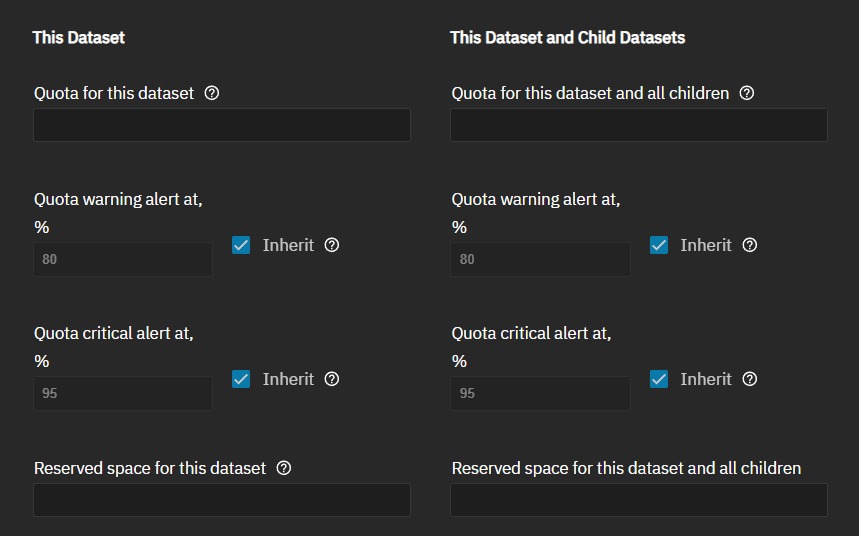
Setting a quota defines the maximum allowed space for the dataset or the dataset and its child datasets. You can reserve a defined amount of pool space to prevent automatically-generated data like system logs from consuming all available dataset space. You can configure quotas for only the new dataset or include all child datasets in the quota.
Quota management settings on the Advanced Options screen set quotas for the selected dataset, and can set the quota for the child datasets of the selected dataset. The Edit button on the dataset Space Management widget opens the Capacity Setting Options for user or group levels can be accessed from the Storage Dashboard screen.
The quota management settings options:
- This Dataset - Sets quotas for only the selected dataset.
- This Dataset and Child Datasets - Sets quotas for the child datasets of the selected dataset.
These settings also display on the Capacity Settings screen that sets quotas at the pool level.
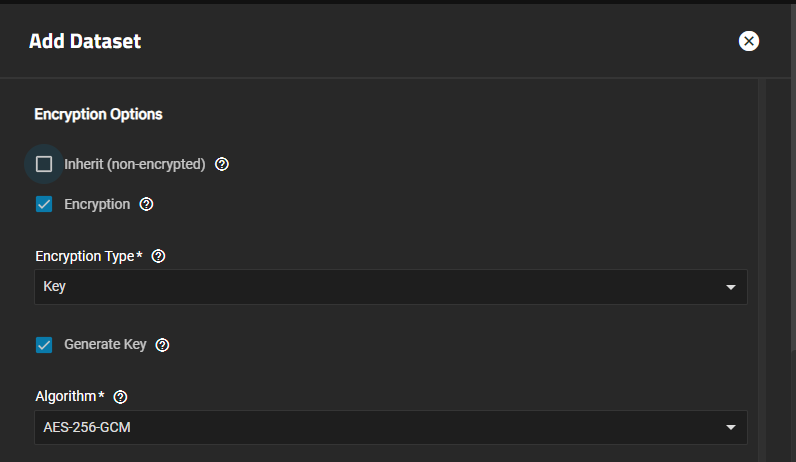
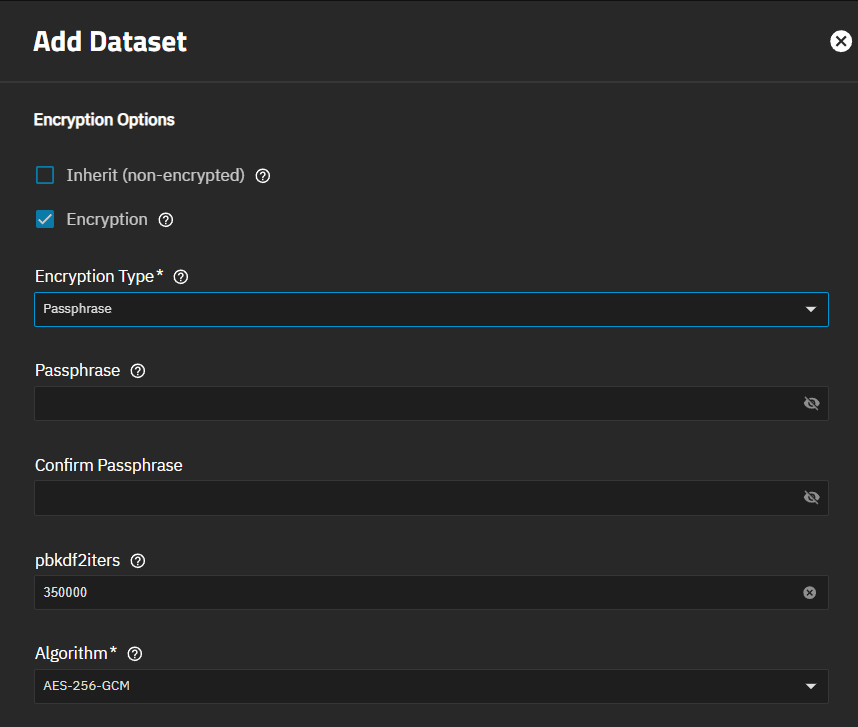
Encryption settings apply key or passphrase type encryption to the selected dataset, and encrypt any child datasets of an encrypted parent. Encryption settings show on in the Advanced Options screen for the Add Dataset screen, but not on the Edit Dataset screen. Edit on the Encryption widget opens the Edit Encryption Options for datasetName window, showing the current encryption settings for the selected dataset and allowing you to change the encryption type settings.
Inherit (Non-Encrypted) shows when you create an unencrypted dataset. Inherit (Encryption) shows when you create an encrypted dataset. All child datasets created under an encrypted dataset are encrypted.
The Encryption option (pre-selected), when selected, shows the key type encryption settings by default. Passphrase in Encryption Type to show other settings.
The Other Options section tunes the dataset for specific data-sharing protocols, sets compression level, sync type options, ACL type and mode, and other settings.
The Compression Level setting lists several compression algorithm to choose from. Select the option that best suits your needs from the dropdown list.
LZ4 maximizes performance and dynamically identifies the best files to compress. LZ4 provides lightning-fast compression/decompression speeds and comes coupled with a high-speed decoder. This makes it one of the best Linux compression tools for enterprise customers.
ZSTD offers highly configurable compression speeds, with a very fast decoder.
Gzip is a standard UNIX compression tool widely used for Linux. It is compatible with every GNU software which makes it a good tool for remote engineers and seasoned Linux users. It offers the maximum compression with the greatest performance impact. The higher the compression level implemented the greater the impact on CPU usage levels. Use with caution especially at higher levels.
ZLE or Zero Length Encoding, leaves normal data alone but only compresses continuous runs of zeros.
LZJB compresses crash dumps and data in ZFS. LZJB is optimized for performance while providing decent compression. LZ4 compresses roughly 50% faster than LZJB when operating on compressible data, and is greater than three times faster for uncompressible data. LZJB was the original algorithm used by ZFS but it is now deprecated.