Active Directory Screens
5 minute read.
The Directory Services screen and widgets provide access to TrueNAS settings to set up access to directory services and advanced authentication systems deployed in user environments.
TrueNAS does not configure Active Directory domain controllers or LDAP directory servers, nor does it configure Kerberos authentication servers or ID mapping systems.
Refer to documentation for these services and systems for information on how to configure each to suit your use case.
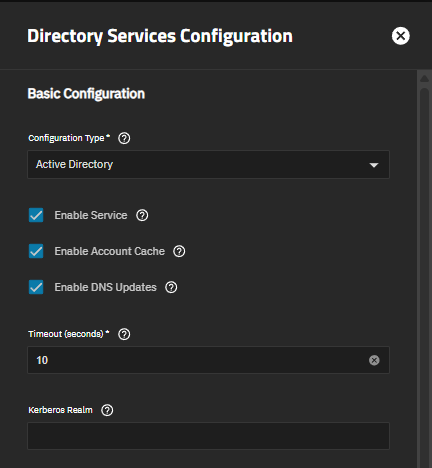
The Active Directory directory service configuration screen shows after selecting Active Directory in the Configuration Type dropdown list in the Directory Services Configuration screen.
For detailed configuration instructions, see Configuring Active Directory.
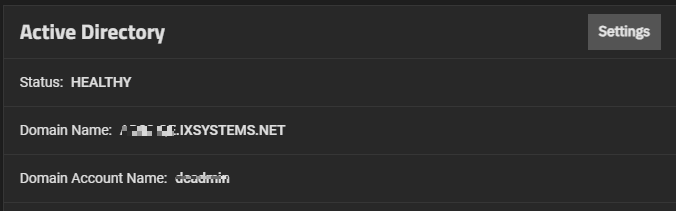
The Active Directory widget displays after configuring TrueNAS to access your Active Directory domain controller. The widget shows Status, Domain Name, and Domain Account Name.
Settings opens the Active Directory configuration screen.
Rebuild Directory Service Cache resyncs the cache if it gets out of sync or if there are fewer users than expected available in the permissions editors.
Leave Domain removes the TrueNAS system from the Active Directory server.
The Directory Services Configuration screen organizes settings into multiple sections: Basic Configuration, Credential Configuration, Active Directory Configuration, Trusted Domains Configuration, and IDMAP Configuration.
The Directory Services Configuration screen is used to configure one of three directory services: Active Directory, IPA, or LDAP. The configuration sections and settings change based on the Configuration Type selected.
The Basic Configuration section settings control core Active Directory service settings.
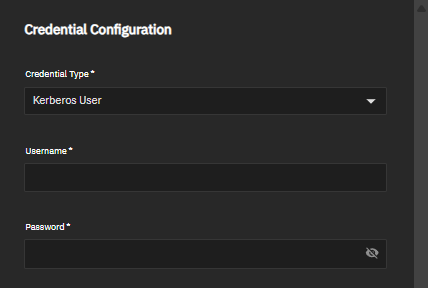
The Credential Configuration section settings define authentication methods for Active Directory access.
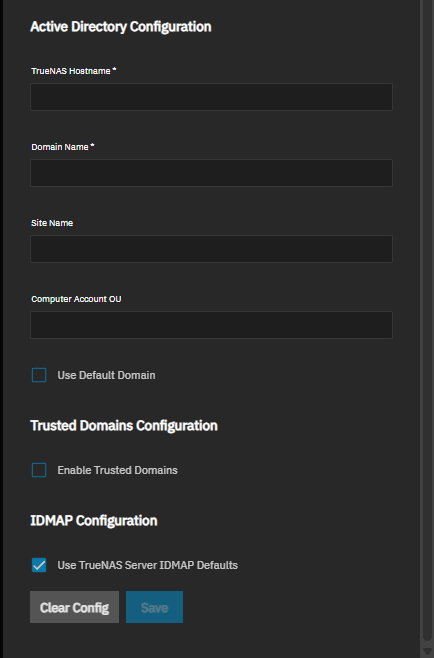
The Active Directory Configuration section settings define the connection parameters and domain-specific options.
The Trusted Domains Configuration section controls access for trusted domains.
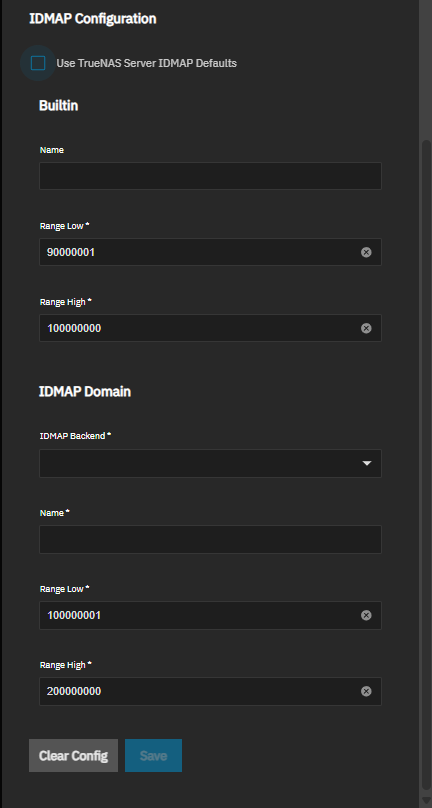
The IDMAP Configuration section controls identity mapping settings.
IDMAP (Identity Mapping) ensures that UIDs and GIDs assigned to Active Directory users and groups have consistent values domain-wide. By default, TrueNAS uses an algorithmic method based on the RID component of the user or group SID, which is suitable for most environments. Only administrators experienced with configuring ID mapping should customize IDMAP settings.