Create Pool
8 minute read.
TrueNAS uses ZFS data storage pools to efficiently store and protect data.
We strongly recommend that you review your available system resources and plan your storage use case before creating a storage pool. Consider the following:
- Allocating more drives to a pool increases redundancy when storing critical information.
- Maximizing total available storage at the expense of redundancy or performance entails allocating large-volume disks and configuring a pool for minimal redundancy.
- Maximizing pool performance entails installing and allocating high-speed SSD drives to a pool.
Security requirements can mean the pool must be created with ZFS encryption. However, we recommend that users create pools as unencrypted and then encrypt some or all of of the child datasets, as needed.
TrueNAS 22.12.3 or later forces encryption for all child datasets and zvols within an encrypted root or parent dataset that are using the TrueNAS UI. However, datasets created outside of the UI, such as those created programmatically or manually via shell access, might not inherit encryption unless properly configured. For more granular control and awareness, we do not recommend users configure pool-level encryption of the root dataset. Instead, create an unencrypted pool and populate it with encrypted or unencrypted child datasets, as needed.
RAIDz pool layouts are well-suited for general use cases and especially smaller (<10) data VDEVS or storage scenarios that involve storing multitudes of small data blocks.
dRAID pool layouts are useful in specific situations where large disk count (>100) arrays need improved resilver times due to increased disk failure rates and the array is intended to store large data blocks.
TrueNAS recommends defaulting to a RAIDz layout generally and whenever a dRAID vdev would have fewer than 10 data storage devices.
Determining your specific storage requirements is a critical step before creating a pool. The ZFS and dRAID primers provide a starting point to learn about the strengths and costs of different storage pool layouts. You can also use the ZFS Capacity Calculator and ZFS Capacity Graph to compare configuration options.
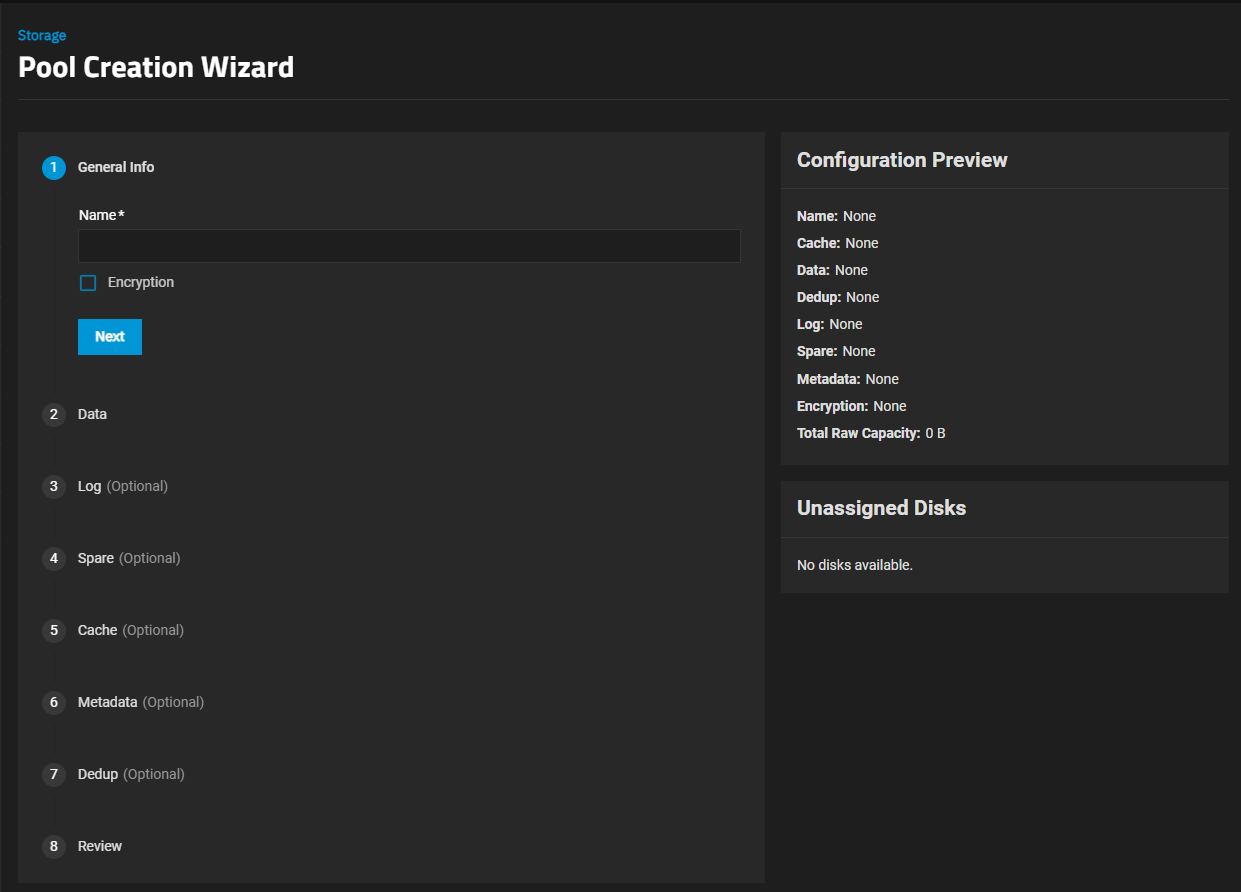
Click Create Pool to open the Pool Creation Wizard.
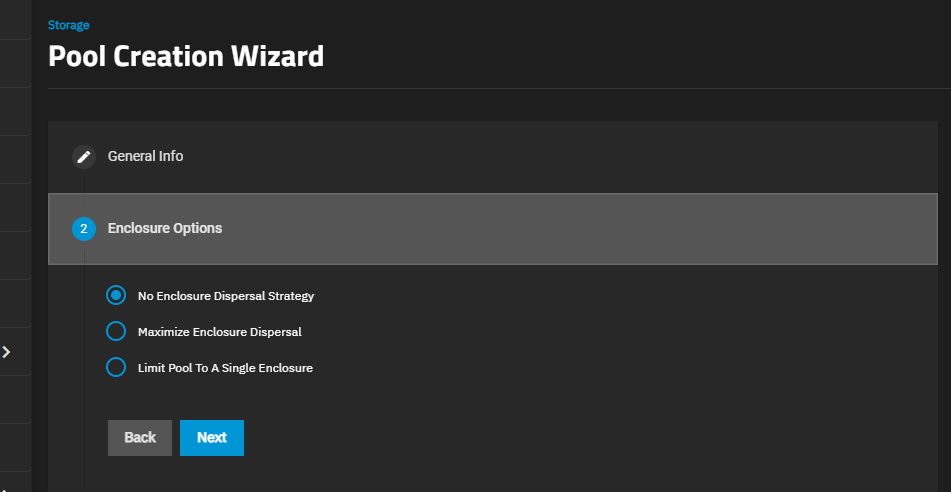
Enclosure Option only shows for TrueNAS Enterprise systems with connected expansion shelves.
You can rename your enclosure on the Enclosure screen to include the rack and U number in the name, which helps identify the physical location while in the pool creation screen.
Enter a name of up to 50 lowercase alpha-numeric characters. Use only the permitted special characters that conform to ZFS naming conventions. The pool name contributes to the maximum character length for datasets, so it is limited to 50 characters.
You cannot change the pool name after creation.(Enterprise systems only) Select the Enclosure Option to apply the dispersal strategy of your choice. This option only shows for TrueNAS Enterprise systems with connected expansion shelves. The dispersal strategy sets how the system adds disks by size and type to the pool VDEVs created using the Automated Disk Selection option. Enclosures mentioned in the options below refer to the disk enclosures in the expansion shelves and main system chassis.
No Enclosure Dispersal Strategy does not apply a dispersal strategy, and does not show additional options. Disks added to the pool VDEVs are assigned in sequence based on disk availability and are not balanced across all enclosures.
Maximum Dispersal Strategy applies a maximum dispersal strategy. This option balances disk selection across all enclosures and available disks and does not show additional options. Disks added to the pool VDEVs are spread across all available enclosure disks.
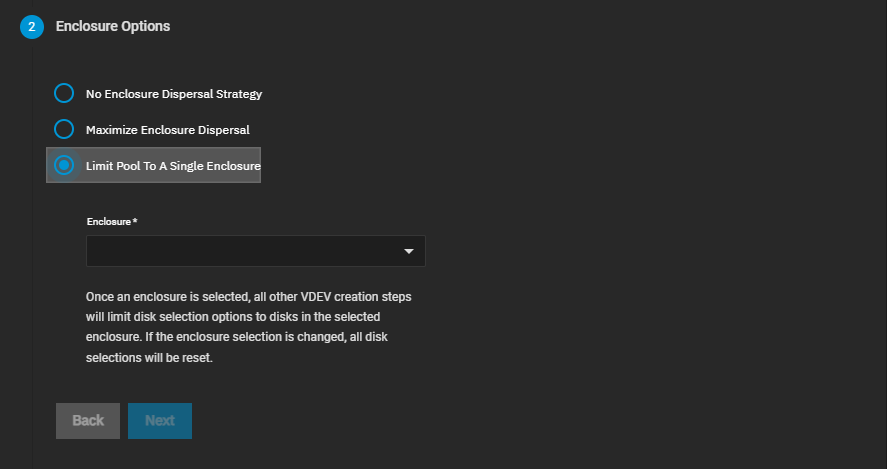
Limit Pool To A Single Enclosure applies a minimum dispersal strategy. Select the expansion shelf option on the Enclosure dropdown. Disks added to the pool VDEVs are spread across the enclosure disks that align with the selection in Enclosure.
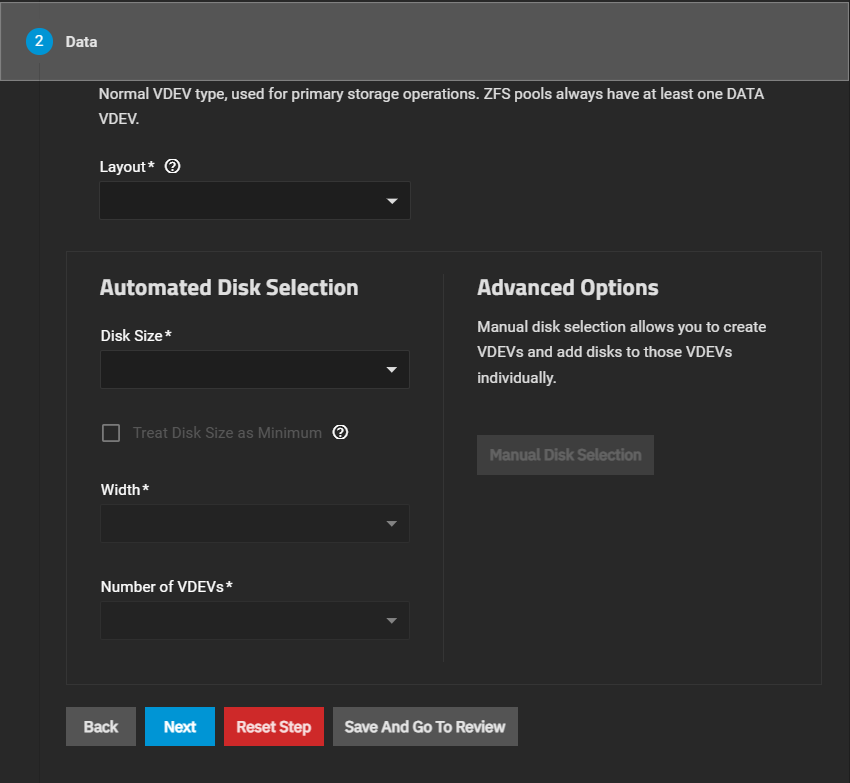
Create the required data VDEV.
Select the layout from the Layout dropdown list, then use the Automated Disk Selection fields to select and add the disks, or click Manual Disk Selection to add specific disks to the chosen Layout.
dRAID layouts do not show the Manual Disk Selection button but do show additional Automated Disk Selection fields. When configuring a dRAID data VDEV, first, choose a Disk Size then select a Data Devices number. The remaining fields update based on the Data Devices and dRAID layout selections.
ZFS allows groups to span multiple rows, which means it does not require each row to contain a whole number of redundancy groups. This layout has several advantages over requiring whole groups in each row:
- Group count - Group count is not a relevant parameter when defining a dRAID layout. ZFS only needs the group width and all groups will have the desired size.
- Group widths - ZFS can support all possible group widths (greater than or equal to the physical disk count).
ZFS determines the number of groups by the least common multiple (LCM) of the group width (D+P) and the number of physical drives minus spares (C-S). The logic within dRAID is simplified when the group width is the same for all groups, although some aspects, such as computing permutation numbers and drive offsets, are more complex. This flexible layout ensures even distribution of data and parity while maintaining high performance and resilvering efficiency.
See vdev_draid.c for more information.
Click Save And Go To Review if not adding other VDEV types to the pool or click Next to move forward to the next wizard screen.
Add optional VDEVs to suit your storage redundancy and performance requirements.
Click Create Pool on the Review wizard screen to add the pool.