Setting Up a Link Aggregation
3 minute read.
In general, a link aggregation (LAGG) is a method of combining (aggregating) multiple network connections in parallel to provide additional bandwidth or redundancy for critical networking situations. TrueNAS uses lagg(4) to manage LAGGs.
Before making network interface changes:
- Stop running apps.
- Power off running virtual machines (VMs) and containers.
- Remove active NIC devices for VMs and containers.
Sharing services such as SMB that use the IP address(s) assigned to the primary interface might cause issues with testing network changes. To resolve issues, stop sharing services such as SMB, change the interface, and test the connection. Restart the service when complete.
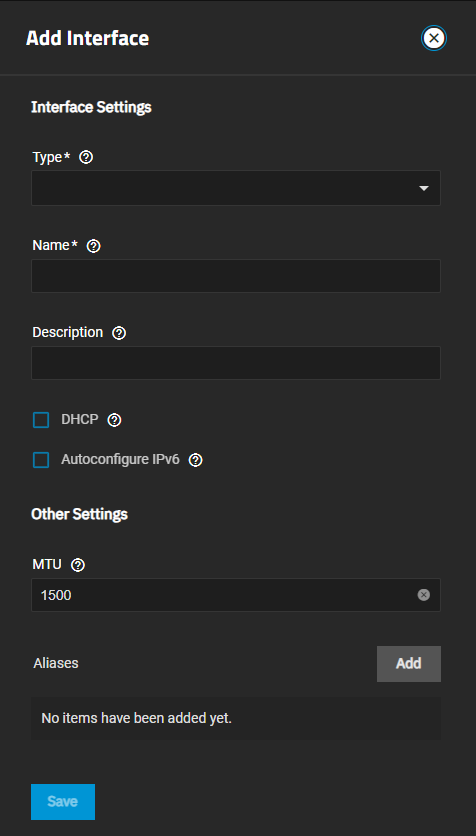
To set up a LAGG, go to Network, click Add on the Interfaces widget to open the Add Interface screen, then:
Select Link Aggregation from the Type dropdown list. You cannot change the Type field value after you click Save.
Enter a name for the interface using the format bondX, where X is a number representing a non-parent interface. Assing the first LAGG interface bond0.
You cannot change the Name of the interface after clicking Apply.
(Optional, but recommended) Enter any notes or reminders about this particular LAGG interface in Description.
Select the protocol from the Link Aggregation Protocol dropdown. Options are LACP, FAILOVER, or LOADBALANCE. Each option displays additional settings.
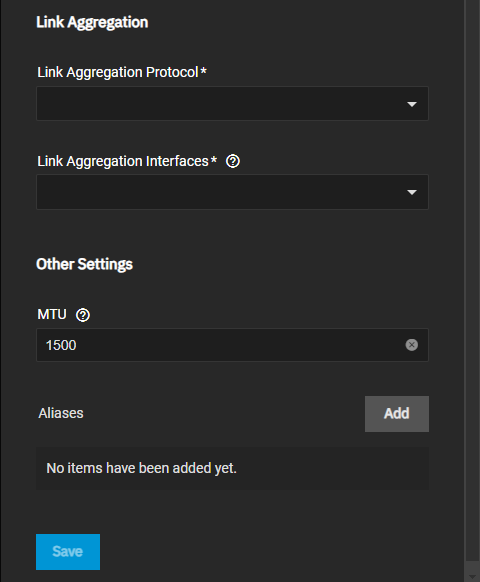
Select the interfaces to use in the aggregation from the Link Aggregation Interface dropdown list.
(Optional) Click Add to the right of Aliases to show additional IP address fields for each additional IP address to add to this LAGG interface.
Click Save when finished.
Test the network change when prompted.