TrueNAS SCALE Documentation Archive
This content follows the TrueNAS SCALE 24.04 (Dragonfish) releases. Archival documentation is provided for reference only and not actively maintained.
Use the Product and Version selectors above to view content specific to different TrueNAS software or major version.
CLI Reference Guide
8 minute read.
The experimental TrueNAS CLI is not recommended for general use and is not receiving further updates in 24.04. As such, the CLI Reference Guide for 24.04 is deprecated and removed.
Please continue to refer to web interface Tutorials for guidance. Thank you!
Welcome to the TrueNAS SCALE Command Line Interface (CLI) guide!
The TrueNAS CLI in TrueNAS SCALE functions like a text-based version of the web UI with many functional areas grouped into parent and child namespaces that mirror the counterparts in the SCALE UI.
The underlying structure of the CLI namespaces and commands closely follows that of the SCALE API. For more information on API commands, arguments, options, and definitions go to API Keys and click on API Docs in the SCALE UI.
The SCALE Shell automatically opens in the SCALE CLI if the admin user Shell setting on the Credentials > Local User > Add User or Edit User screen is set to TrueNAS CLI.
If set to a different shell option such as bash or zsh, enter cli at the prompt on the shell screen.
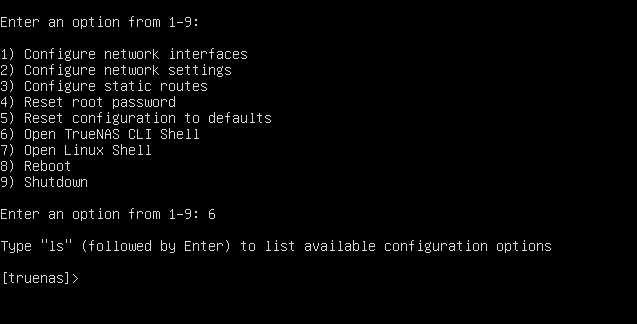
You can also access the TrueNAS CLI through the Console Setup Menu.
You can access the Console Setup Menu when you SSH into the TrueNAS system after you install SCALE from the
To open the TrueNAS CLI from the Console Setup Menu, enter 6.
The Shell screen opens in the shell option selected in the Shell setting on the Credentials > Local User > Add User or Edit User screen. Options are nologin, TrueNAS CLI, TrueNAS Console, sh, bash, rbash, dash, tmux, and zsh.
To access the TrueNAS CLI from the Linux shell, enter cli at the prompt and press Enter.
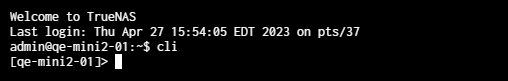
To exit the TrueNAS CLI, enter quit or exit.
The SCALE CLI includes help text for some namespaces and commands through the both the man, and ls commands.
To see the basic commands from any namespace, enter help.
Use the man command to show the help text for a namespace or command with options.
Type man namespacename or man commandname to display the help text for that namespace or command.
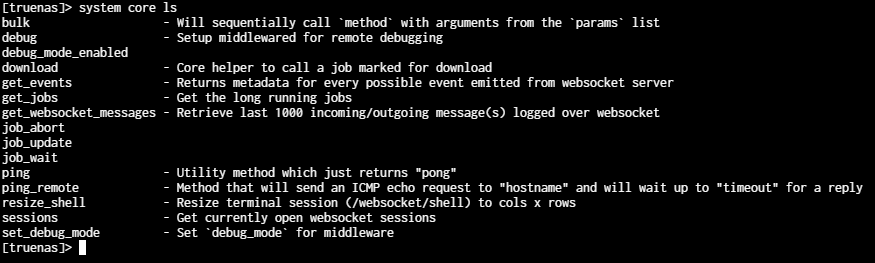
Use the ls command while in a child namespace to view a list of commands and the help text descriptions.
You can use the ls command for some commands that show an autofill list of options to display a list of those options with help text descriptions.
Note, not all namespaces, commands, or commands with options include help text.
Using ls with some commands with autofill options does not always display a list view or help text for the options.
The TrueNAS CLI includes basic commands available from the CLI prompt or while in any namespace in the CLI.
To access these basic options, enter ? or help, then press Enter. The list of basic commands displays.
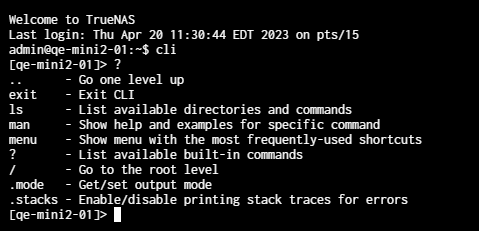
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
.. | Moves up one level. For example, from a namespace like auth, enter .. to return to the CLI prompt. From a child namespace like interfaces, use .. to return to the network parent namespace. |
exit | Leave the TrueNAS CLI and return to the system prompt. |
ls | Lists the namespaces and commands from the active CLI level. For example, at the top level, ls displays the main namespaces in the TrueNAS CLI. At a main namespace level, ls displays the additional namespaces or commands for that level. |
man | When in a namespace, displays the help text for the command that follows man. For example, while in the network namespace, enter man create to see the help text for the create command. |
menu | Displays the Console setup menu in the TrueNAS CLI. Type 6 to exit the menu and return to the CLI prompt. |
? | Displays the list of basic commands for the TrueNAS CLI. |
/ | Returns to the main TrueNAS CLI prompt from any namespace. |
.mode | Gets or sets the output mode. |
.stacks | Enables/disables printing stack traces for errors. |
The TrueNAS CLI provides eleven top-level (parent) namespaces that correspond to SCALE UI functions but not all namespaces mirror the UI counterpart. For example, the system namespace includes alerts and certificates in the CLI but in the UI the counterpart is System Settings, and neither Alerts or Certificates are found under System Settings. Each parent namespace has child namespaces and commands.
Use the ls command to view the list of namespaces or commands.

| Namespace | Description |
|---|---|
| account | Provides access to the user and group namespaces and commands. In the UI these are found on the **Credentials screen. |
| app | Provides access to the catalog, chart_release, container, docker and kubernetes namespaces and commands. |
| auth | Provides access to the authentication api_key, privilege, sessions, and two_factor namespaces and commands. |
| directory_service | Provides access to directory services activedirectory, idmap, kerberos, and ldap namespaces and commands. |
| filesystem | Provides access to the acltemplate namespace. |
| network | Provides access to network configuration, dns, interface, ipmi, route, and static_route namespaces and commands. |
| service | Provides access to service ftp, ipmi, nfs, smart, smb, snmp, ssh, and vm namespaces and commands. |
| sharing | Provides access to sharing iscsi, nfs, and smb namespaces and commands. |
| storage | Provides access to storage dataset, disk, enclosure, filesystem, pool, resilver, scrub, snapshot, and vmware namespaces and commands. |
| system | Provides access system acme, advanced, alert, boot, bootenv, certificate, config, core, failover, general, keychain_credential, kmip, mail, ntp_server, reporting, support, system_dataset, truecommand, truenas, tunable, update, and version namespaces and commands. |
| task | Provides access to task cloud_sync, cron_job, replication, rsync, smart_test, and snapshot namespaces and commands. |
CLI namespaces and commands are case-sensitive. Enter commands in lowercase unless the CLI autofill indicates otherwise.
To enter a namespace or command, begin typing the name. The CLI displays an autofill list that begins with the letter typed and is available in that part of the CLI. Press the down arrow to select the name of the command or namespace. For example, the autofill list at the main CLI prompt includes only the parent namespaces that begin with the letter typed.
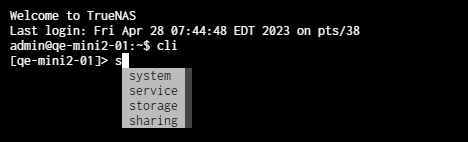
To enter a basic command such as checking current configuration settings in a namespace, enter namespace childnamespace config.
The system displays the configured settings for the namespaces preceding the config command.
You can enter a namespace, child namespace, command, command properties (options), and arguments (property=value pairs) from the main CLI prompt using autofill options.
For example, parent namespace child namespace command property=value.
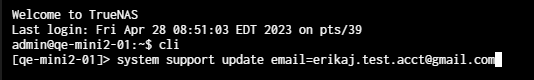
You can enter a namespace, child namespace, and the command, then select the command property to enter the argument (property=value) from the namespace prompt.

A command without properties does not show an autofill list. Press space to see if the command has more properties or wants input or press Enter to apply the command.
To go up one namespace or command level, enter ...
Enter / to return to the main CLI prompt and exit the namespace(s).
Use the up or down arrow keys to select an autofill option, then press space to apply it.
You can use Backspace to erase entered text to start over.
Use the left arrow to move the cursor to the left in a command string where you change the text or use Delete to remove anything to the right of the cursor.
Use the right arrow to move the cursor to the right to the end of the command string to either continue entering command options or to press Enter to apply the command.
TrueNAS CLI command structure varies by namespace. CLI commands can include properties (options) and/or arguments (property=value pairs) and might include flags.
Command properties that require a single value automatically add the = delimiter after the property on the autofill list and after reaching the end of the command property inputs.
Some commands allow entering multiple arguments enclosed in curly brackets. These curly brackets could enclose multiple arguments in square brackets separated by a comma and space.
Argument properties (options) and values might require double quotes around each, and are separated by a colon : instead of the equal sign.
Each namespace article includes command syntax examples for each namespace.
Enter the -- flag following any CLI command to open the interactive arguments editor text-based user interface (TUI).
TrueNAS has eleven primary or parent namespaces. Some of the primary namespaces include commands as well as having child namespaces. Each child namespace has commands to perform various actions.
- ⎙ Download or Print: View the entire CLI Reference Guide as a single page for download or print.