TrueNAS Documentation Archive
This content follows the TrueNAS 23.10 (Cobia) releases. Archival documentation is provided for reference only and not actively maintained. Use the Product and Version selectors above to view content specific to different TrueNAS software or major version.
Adding and Managing VMs
8 minute read.
Last Modified 2024-03-19 08:38 EDTA virtual machine (VM) is an environment on a host computer that you can use as if it is a separate, physical computer. Users can use VMs to run multiple operating systems simultaneously on a single computer. Operating systems running inside a VM see emulated virtual hardware rather than the host computer physical hardware. VMs provide more isolation than Jails but also consume more system resources.
Before creating a VM, you need an installer
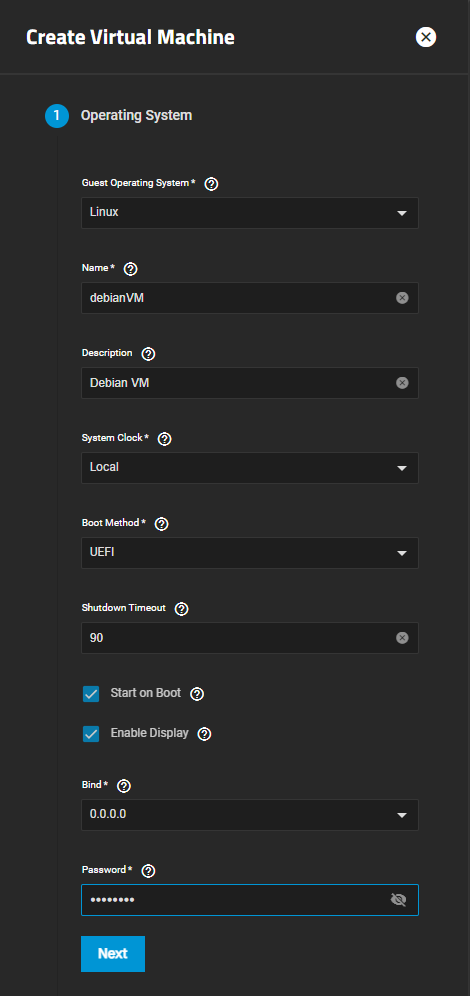
To create a new VM, go to Virtualization and click Add to open the Create Virtual Machine configuration screen. If you have not yet added a virtual machine to your system you can click Add Virtual Machines to open the same screen.
Select the operating system you want to use from the Guest Operating System dropdown list.
Compare the recommended specifications for the guest operating system with your available host system resources when allocating virtual CPUs, cores, threads, and memory size.
Change other Operating System settings per your use case.
Select UTC as the VM system time from the System Clock dropdown if you do not want to use the default Local setting.
Change the default IP address in Bind if you want use a specific address as the primary network interface, otherwise leave it set to 0.0.0.0.
If selecting Enable Display, enter a device Password.
Click Next.
Enter the CPU and memory settings for your VM.
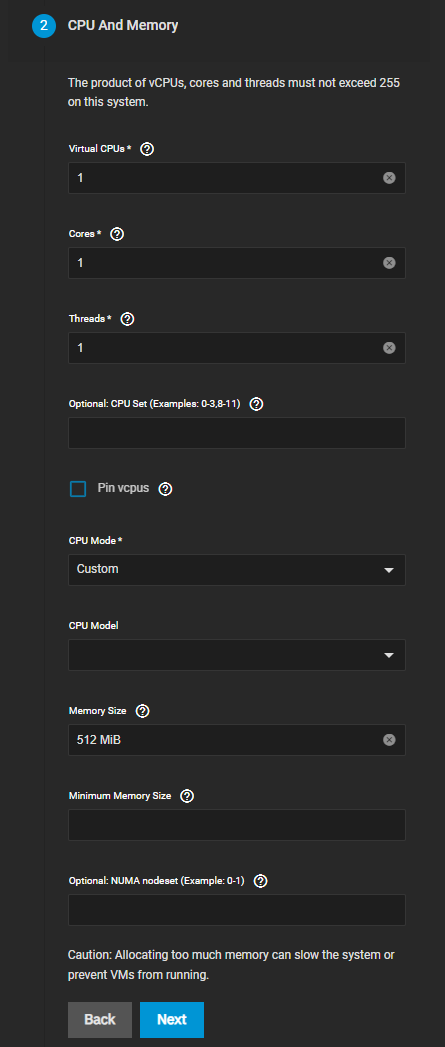
If you selected Windows as the Guest Operating System, the Virtual CPUs field displays a default value of 2. The VM operating system might have operational or licensing restrictions on the number of CPUs.
Do not allocate too much memory to a VM. Activating a VM with all available memory allocated to it can slow the host system or prevent other VMs from starting.
Leave CPU Mode set to Custom if you want to select a CPU model.
Specify the amount of RAM you want for the VM if you want to use more or less than the default. We recommend increasing this value, but your configuration depends on the resources available for your VM.
Click Next.
Configure disk settings.
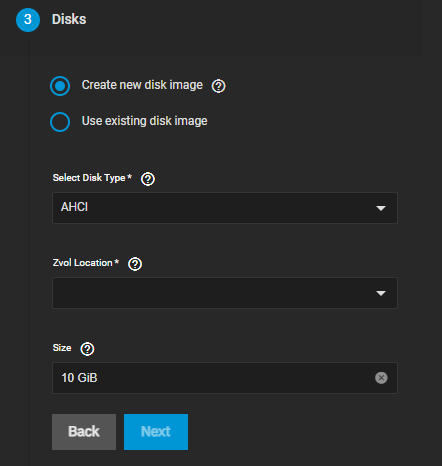
Select Create new disk image to create a new zvol on an existing dataset.
Select Use existing disk image to use an existing zvol for the VM.Select either AHCI or VirtIO from the Select Disk Type dropdown list. We recommend using AHCI or Windows VMs.
Select the location for the new zvol from the Zvol Location dropdown list.
Enter a value in Size (Examples: 500KiB, 500M, and 2TB) to indicate the amount of space to allocate for the new zvol.
Click Next.
Configure the network interface.
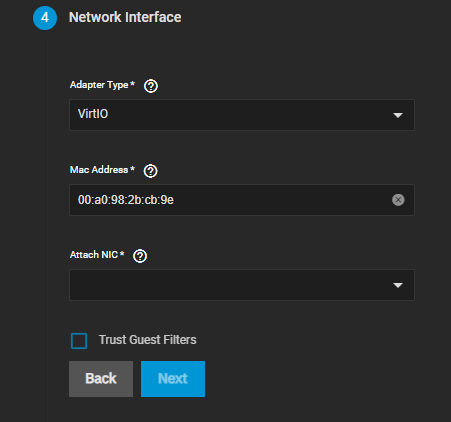
Select the network interface type from the Adapter Type dropdown list. Select Intel e82585 (e1000) as it offers a higher level of compatibility with most operating systems, or select VirtIO if the guest operating system supports para-virtualized network drivers.
Select the network interface card to use from the Attach NIC dropdown list.
Click Next.
Upload installation media for the operating system you selected.
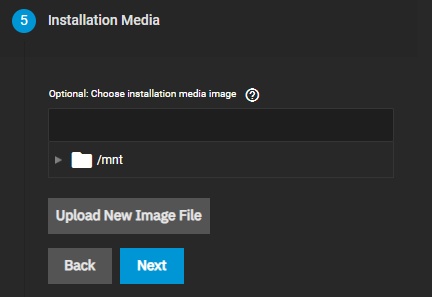
You can create the VM without an OS installed. To add it either type the path or browse to the location and select it.
To upload an
iso select Upload New Image File and either enter the path or browse to the location of the file.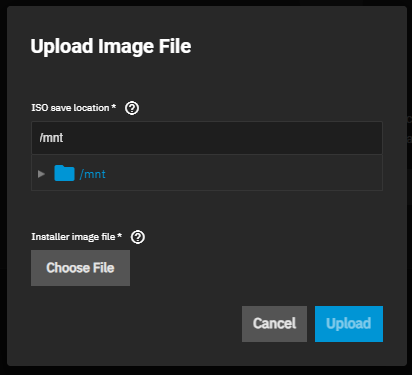
Click Upload to begin the upload process. After the upload finishes, click Next.
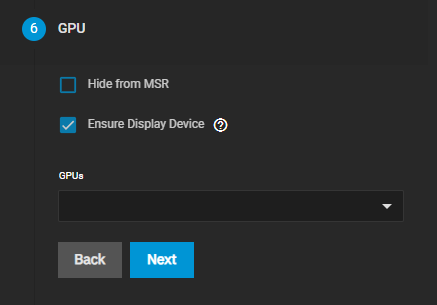
Specify a GPU.
The VirtIO network interface requires a guest OS that supports VirtIO para-virtualized network drivers.
iXsystems does not have a list of approved GPUs at this time but does have drivers and basic support for the list of nvidia Supported Products.Confirm your VM settings, then click Save.
After creating the VM, you can add or remove virtual devices.
Expand the VM entry on the Virtual Machines screen and click device_hub Devices.
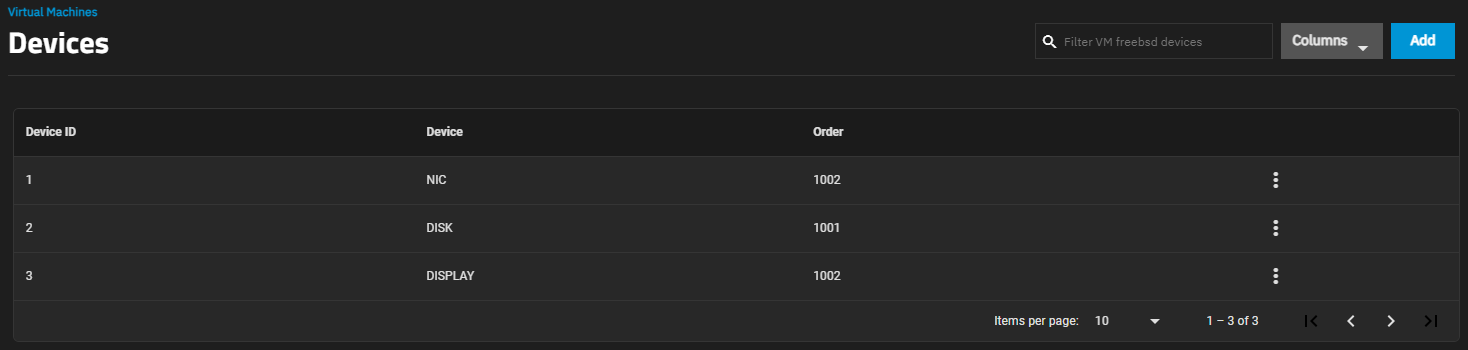
Device notes:
- A virtual machine attempts to boot from devices according to the Device Order, starting with 1000, then ascending.
- A CD-ROM device allow booting a VM from a CD-ROM image like an installation CD. The CD image must be available in the system storage.
After creating the VM and configuring devices for it, manage the VM by expanding the entry on the Virtual Machines screen.
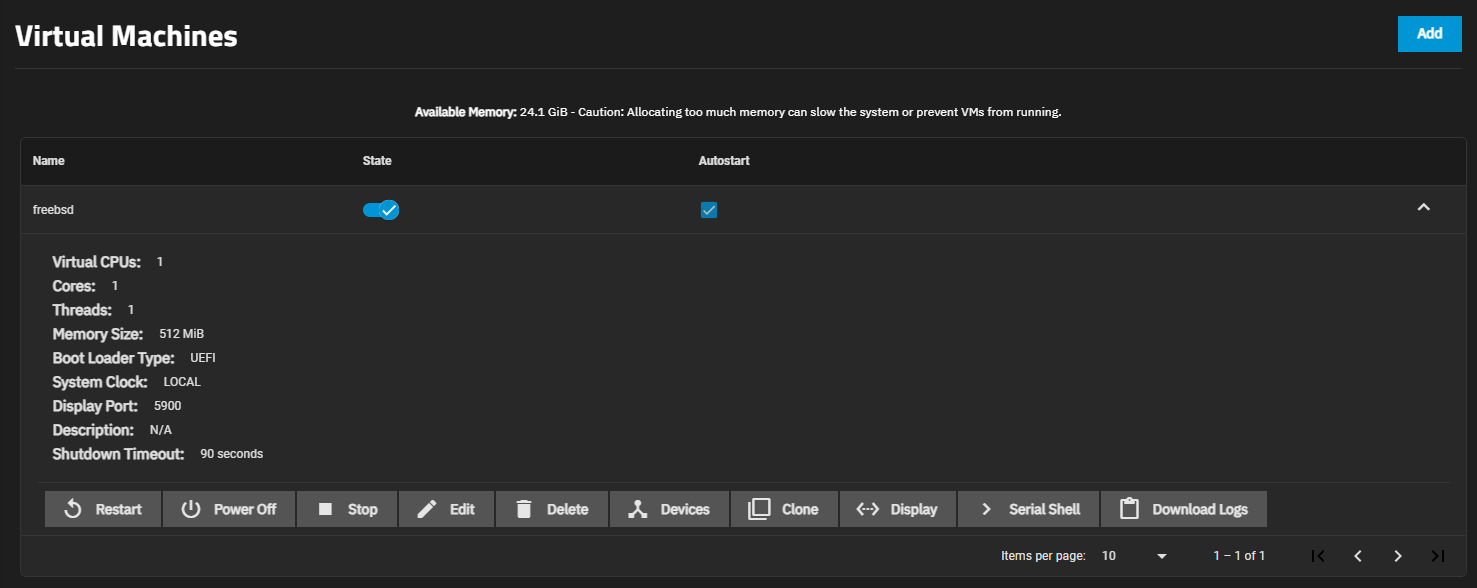
An active VM displays options for settings_ethernet Display and keyboard_arrow_right Serial Shell connections.
When a Display device is configured, remote clients can connect to VM display sessions using a SPICE client, or by installing a 3rd party remote desktop server inside your VM. SPICE clients are available from the SPICE Protocol site.
If the display connection screen appears distorted, try adjusting the display device resolution.
Use the State toggle or click stop Stop to follow a standard procedure to do a clean shutdown of the running VM. Click power_settings_new Power Off to halt and deactivate the VM, which is similar to unplugging a computer.
If the VM you created has no Guest OS installed, The VM State toggle and stop Stop button might not function as expected. The State toggle and stop Stop button send an ACPI power down command to the VM operating system, but since an OS is not installed, these commands time out. Use the Power Off button instead.
When the VM is configured in TrueNAS and has an OS
Some operating systems can require specific settings to function properly in a virtual machine. For example, vanilla Debian can require advanced partitioning when installing the OS. Refer to the documentation for your chosen operating system for tips and configuration instructions.