TrueNAS Documentation Archive
This content follows the TrueNAS 23.10 (Cobia) releases. Archival documentation is provided for reference only and not actively maintained. Use the Product and Version selectors above to view content specific to different TrueNAS software or major version.
Adding and Managing Datasets
7 minute read.
Last Modified 2024-03-19 08:38 EDTA TrueNAS dataset is a file system within a data storage pool. Datasets can contain files, directories (child datasets), and have individual permissions or flags. Datasets can also be encrypted, either using the encryption created with the pool or with a separate encryption configuration.
We recommend organizing your pool with datasets before configuring data sharing, as this allows for more fine-tuning of access permissions and using different sharing protocols.
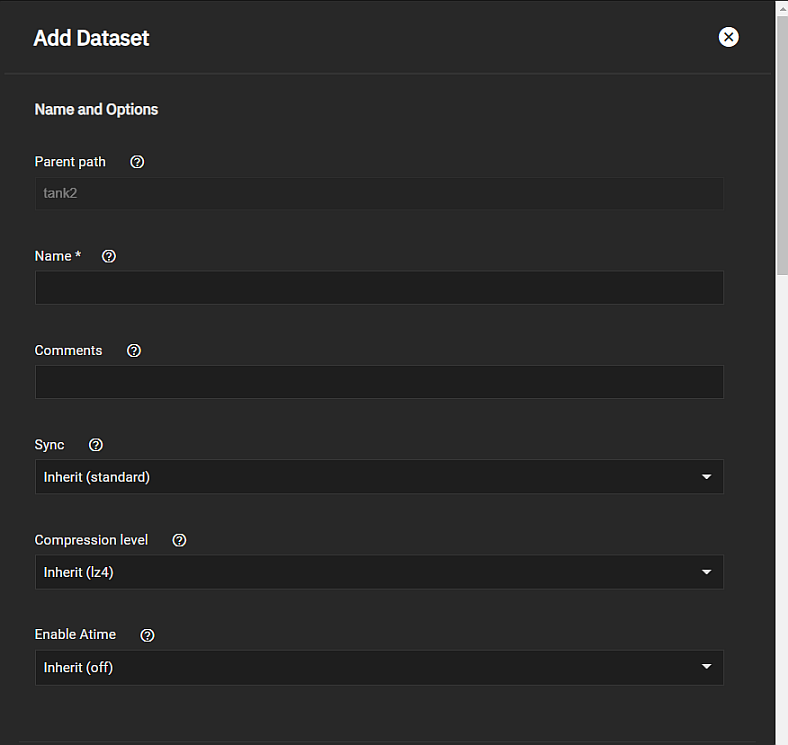
To create a dataset using the default settings, go to Datasets. Default settings include the settings datasets inherit from the parent dataset.
Select a dataset (root, parent, or child), then click Add Dataset.
Enter a value in Name.
Select either Sensitive or Insensitive from the Case Sensitivity dropdown.
Select the Share Type, then click Save. Options are Generic, Multiprotocol, SMB, or Apps.
You can create datasets optimized for SMB shares or with customized settings for your dataset use cases.
If you plan to deploy container applications, the system automatically creates the ix-applications dataset, but it is not used for application data storage. If you want to store data by application, create the dataset first, then deploy your application. When creating a dataset for an application, select App as the Share Type setting. This optimizes the dataset for use by an application.
Review the Share Type and Case Sensitivity options on the configuration screen before clicking Save. You cannot change these or the Name setting after clicking Save.
Compression encodes information in less space than the original data occupies. We recommended you choose a compression algorithm that balances disk performance with the amount of saved space.
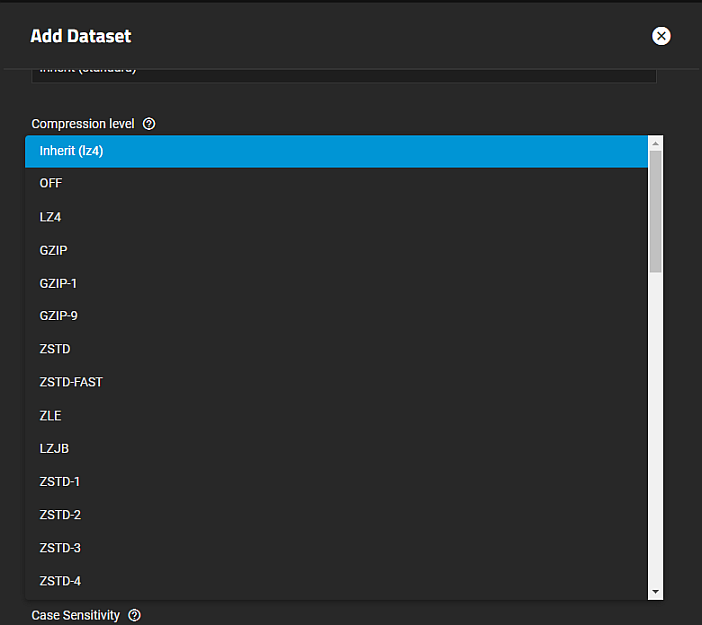
Select the compression algorithm that best suits your needs from the Compression dropdown list of options.
LZ4 maximizes performance and dynamically identifies the best files to compress. LZ4 provides lightning-fast compression/decompression speeds and comes coupled with a high-speed decoder. This makes it one of the best Linux compression tools for enterprise customers.
ZSTD offers highly configurable compression speeds, with a very fast decoder.
Gzip is a standard UNIX compression tool widely used for Linux. It is compatible with every GNU software which makes it a good tool for remote engineers and seasoned Linux users. It offers the maximum compression with the greatest performance impact. The higher the compression level implemented the greater the impact on CPU usage levels. Use with caution especially at higher levels.
ZLE or Zero Length Encoding, leaves normal data alone but only compresses continuous runs of zeros.
LZJB compresses crash dumps and data in ZFS. LZJB is optimized for performance while providing decent compression. LZ4 compresses roughly 50% faster than LZJB when operating on compressible data, and is greater than three times faster for uncompressible data. LZJB was the original algorithm used by ZFS but it is now deprecated.
You can set dataset quotas when you add a dataset using the Add Dataset > Advanced Options quota management options, or to add or edit quotas for a selected dataset, click Edit on the Dataset Space Management widget to open the Capacity Settings screen.
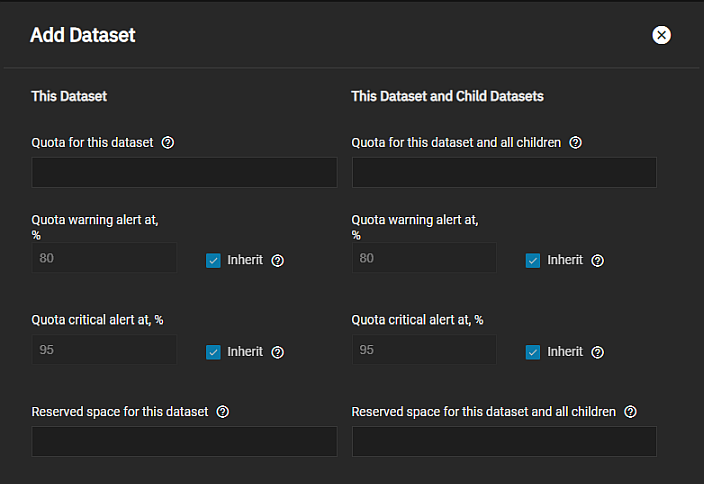
Setting a quota defines the maximum allowed space for the dataset. You can also reserve a defined amount of pool space to prevent automatically generated data like system logs from consuming all of the dataset space. You can configure quotas for only the new dataset or for both the new dataset and any child datasets of the new dataset.
Define the maximum allowed space for the dataset in either the Quota for this dataset or Quota for this dataset and all children field. Enter 0 to disable quotas.
Dataset quota alerts are based on the percentage of used storage. To set up a quota warning alert, enter a percentage value in Quota warning alert at, %. When consumed space reaches the defined percentage it sends the alert. To change the setting from the parent dataset warning level, clear the Inherit checkbox and then change the value.
To set up the quota critical level alerts, enter the percentage value in Quota critical alert at, %. Clear the Inherit checkbox to change this value to something other than using the parent alert setting.
When setting quotas or changing the alert percentages for both the parent dataset and all child datasets, use the fields under This Dataset and Child Datasets.
Enter a value in Reserved space for this dataset to set aside additional space for datasets that contain logs which could eventually take all available free space. Enter 0 for unlimited.
For more information on quotas, see Managing User or Group Quotas.
By default, many of dataset options inherit their values from the parent dataset. When you select Inherit, as a checkbox or option in a dropdown list, the dataset uses the setting from the parent dataset. For example, the Encryption or ACL Type settings.
To change any setting that can inherit the parent setting, clear the checkbox or select another available option, and then enter the desired setting values for the child dataset.
For information on ACL settings see Setting Up Permissions.
First, add a Metadata VDEV to the pool.
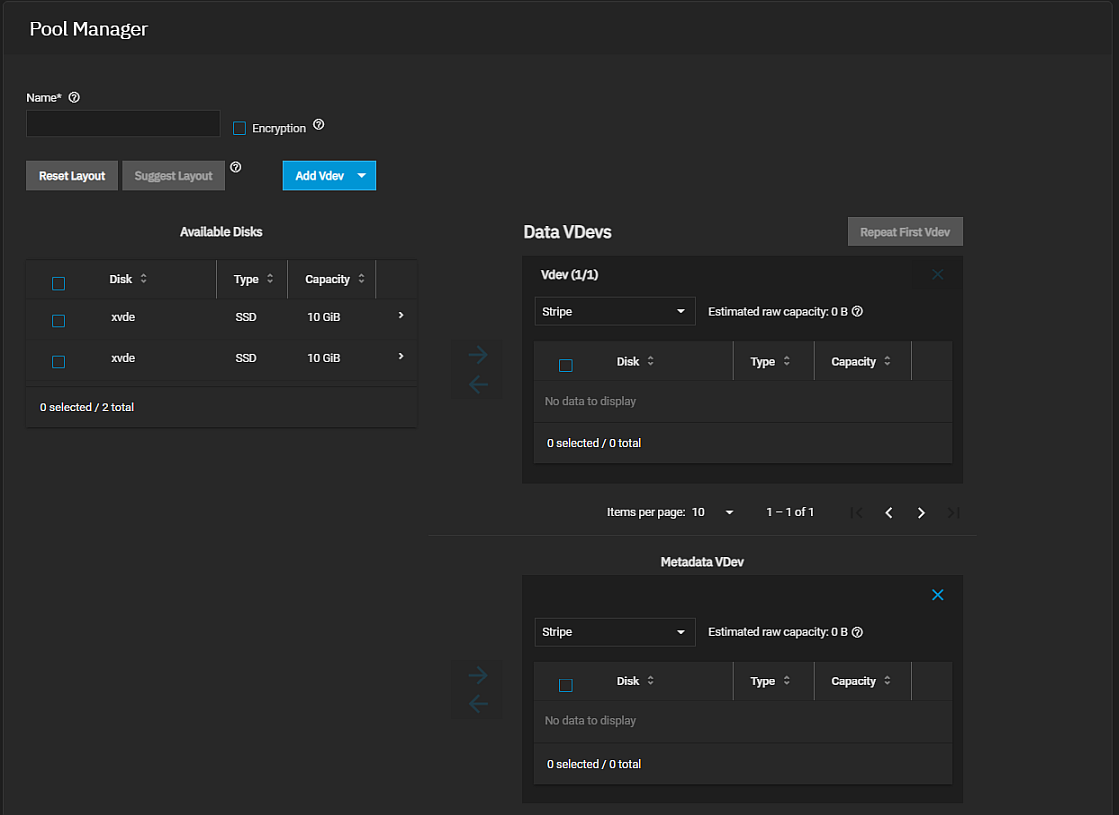
Then add the dataset. Use the Metadata (Special) Small Block Size setting on the Add Dataset > Advanced Options > Other Options screen to set a threshold block size for including small file blocks into the special allocation class (fusion pools).
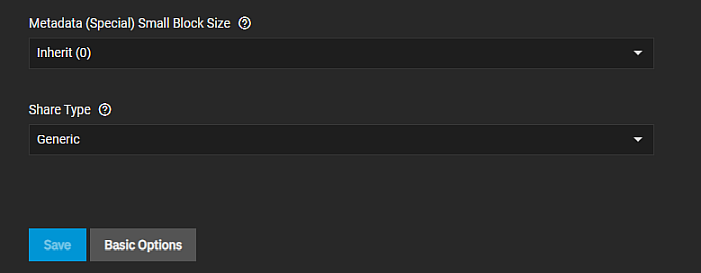
Blocks smaller than or equal to this value are assigned to the special allocation class while greater blocks are assigned to the regular class. Valid values are zero or a power of two from 512B up to 1M. The default size 0 means no small file blocks are allocated in the special class. Enter a threshold block size for including small file blocks into the special allocation class (fusion pools).
After creating a dataset, users can manage additional options from the Datasets screen. Select the dataset you want to manage, then click Edit on the widget for the function you want to manage. The Datasets Screen article describes each option in detail.
Select the dataset on the tree table, then click Edit on the Dataset Details widget to open the Edit Dataset screen and change the dataset configuration settings. You can change all settings except Name, Case Sensitivity, or Share Type.
The Permissions widget for a dataset with an NFSv4 ACL type, converts each listed ACL item a button that opens a permissions editor for that ACL item. To configure new ACL items for an NFSv4 ACL, click Edit to open the ACL Editor screen.
To edit a POSIX ACL type, click Edit on the Permissions widget to open the Unix Permissions Editor screen.
For more information, see the Setting Up Permissions article.
Select the dataset on the tree table, then click Delete on the Dataset Details widget. This opens a window where you enter the path (parent/child) and select Confirm to delete the dataset, all stored data, and any snapshots from TrueNAS.
To delete a root dataset, use the Export/Disconnect option on the Storage Dashboard screen to delete the pool.
Deleting datasets can result in unrecoverable data loss! Move off any critical data stored on the dataset or obsolete it before performing the delete operation.
Related Content
- Dataset
- Advanced Settings Screen
- Capacity Settings Screen
- Managing User or Group Quotas
- Snapshots Screen
- User and Group Quota Screens
- Snapshot
- Encryption Settings
- Storage Encryption