TrueNAS Documentation Archive
This content follows the TrueNAS 23.10 (Cobia) releases. Archival documentation is provided for reference only and not actively maintained. Use the Product and Version selectors above to view content specific to different TrueNAS software or major version.
Multiprotocol Shares
10 minute read.
Last Modified 2024-04-24 14:31 EDTA multiprotocol or mixed-mode NFS and SMB share supports both NFS and SMB protocols for sharing data. Multiprotocol shares allow clients to use either protocol to access the same data. This can be useful in environments with a mix of Windows systems and Unix-like systems, especially if some clients lack an SMB client.
Carefully consider your environment and access requirements before configuring a multiprotocol share. For many applications, a single protocol SMB share provides better user experience and ease of administration. Linux clients can access SMB shares usingmount.cifs.
It is important to properly configure permissions and access controls to ensure security and data integrity when using mixed-mode sharing. To maximize security on the NFS side of the multiprotocol share, we recommend using NFSv4 and Active Directory (AD) for Kerberos authentication. It is also important that NFS clients preserve extended attributes when copying files, or SMB metadata could be discarded in the copy.
Before adding a multiprotocol SMB and NFS share to your system:
Configure and start the SMB and NFS services. Ensure that NFS is configured to require Kerberos authentication.
Join the TrueNAS server to an existing Active Directory domain. Configure a container, Kerberos admin, and user accounts in AD.
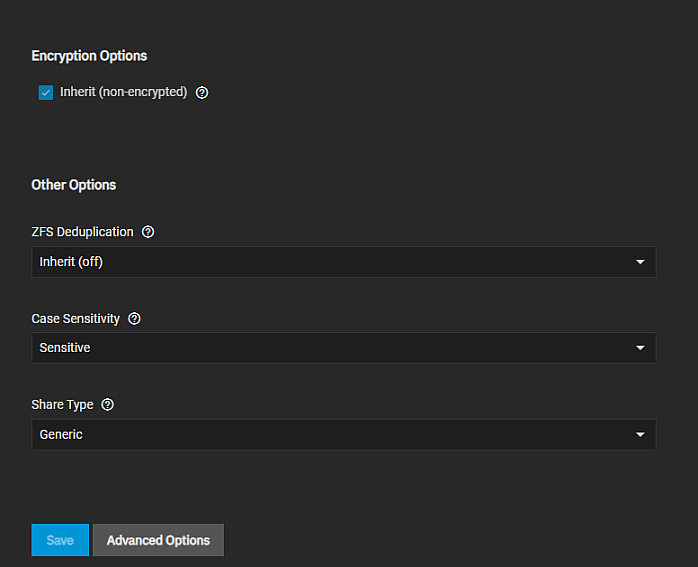
Set up a dataset for the new share with Share Type set to Multiprotocol.
Before joining AD and creating a dataset for the share to use, first start both the SMB and NFS services and configure the NFS Service for Kerberos authentication. Configure the NFS service before joining AD for simpler Kerberos credential creation.
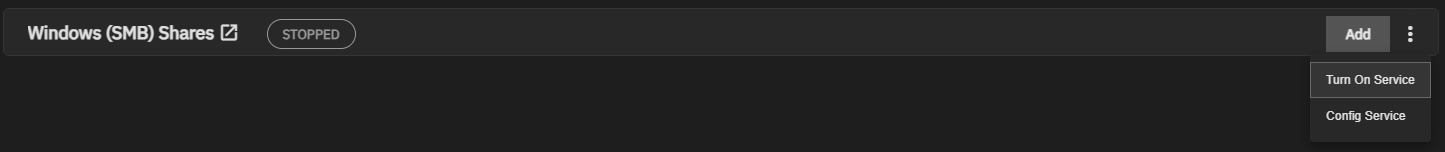
Configure the SMB service by clicking Config Service from the dropdown menu on the Shares screen or by clicking edit on the Services screen. Unless you need a specific setting or are configuring a unique network environment, we recommend using the default settings.
Start the service from the Windows SMB Share header on the Sharing screen or in System Settings > Services.
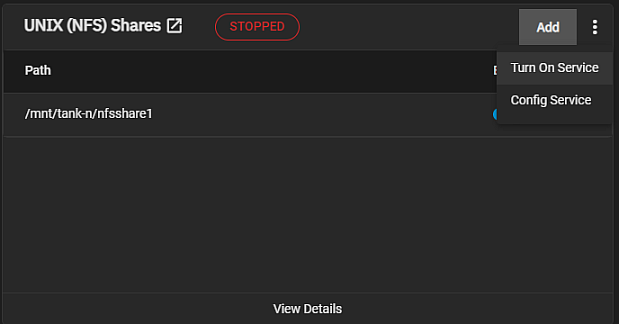
Configure the NFS service by clicking Config Service from the dropdown menu on the Shares screen or by clicking edit on the Services screen.
Under NFSv4, ensure the NFSv4 protocol is selected from the Enabled Protocols dropdown menu. For security hardening, we recommend disabling the NFSv3 protocol.
Select Require Kerberos for NFSv4 to enable using a Kerberos ticket.
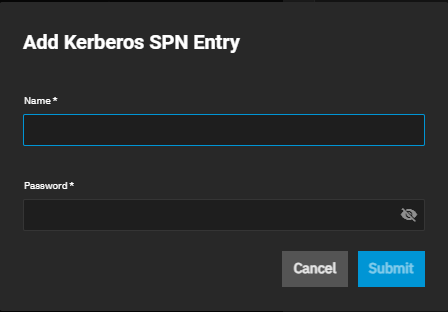
If Active Directory is already joined to the TrueNAS server, click Save and then reopen the NFS configuration screen. Click Add SPN to open the Add Kerberos SPN Entry dialog.
Click Yes when prompted to add a Service Principal Name (SPN) entry. Enter the AD domain administrator user name and password in Name and Password.
TrueNAS SCALE automatically applies SPN credentials if the NFS service is enabled with Require Kerberos for NFSv4 selected before joining Active Directory.
Start the service from the Unix Shares (NFS) header on the Sharing screen or in System Settings > Services.
Mixed-mode SMB and NFS shares greatly simplify data access for client running a range of operating systems. They also require careful attention to security complexities not present in standard SMB shares. NFS shares do not respect permissions set in the SMB Share ACL. Protect the NFS export with proper authentication and authorization controls to prevent unauthorized access by NFS clients.
We recommend using Active Directory to enable Kerberos security for the NFS share. Configure a container (group or organizational unit), Kerberos admin, and user accounts in AD.
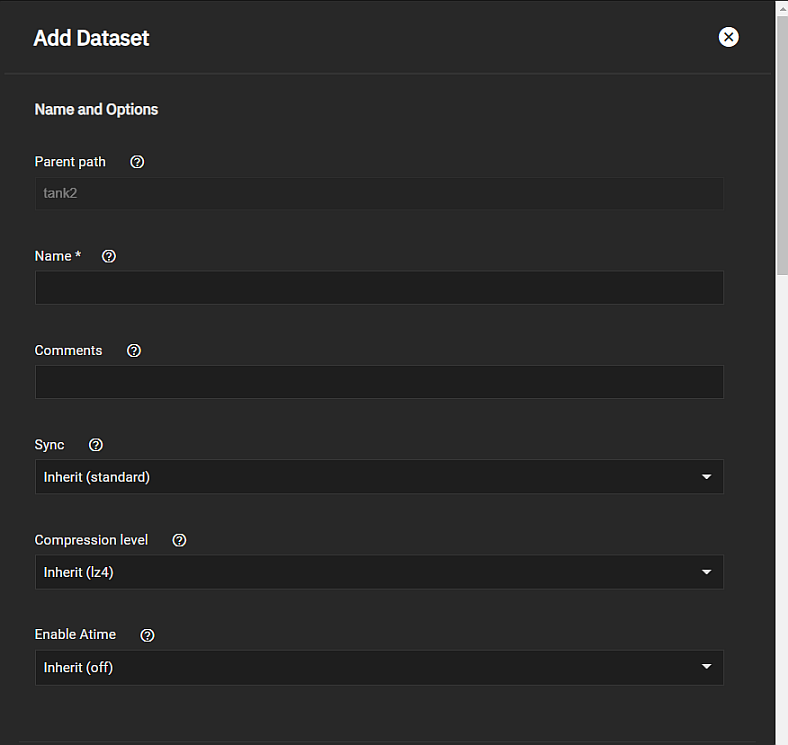
Before creating a mixed-mode share, create the dataset you want the share to use for data storage.
It is best practice to use a dataset instead of a full pool for SMB and/or NFS shares. Sharing an entire pool makes it more difficult to later restrict access if needed.
We recommend creating a new dataset with the Share Type set to Multiprotocol for the new mixed-mode share.
After joining AD and creating a dataset, adjust the dataset/file system ACL to match the container and users configured in AD.
To configure a multiprotocol share on your system:
Complete the first steps above.
Create the SMB share with Purpose set to Multi-protocol (NFSv4/SMB) shares.
Create the NFS share with Security set to KRB5.
Connect client system(s) to the share.
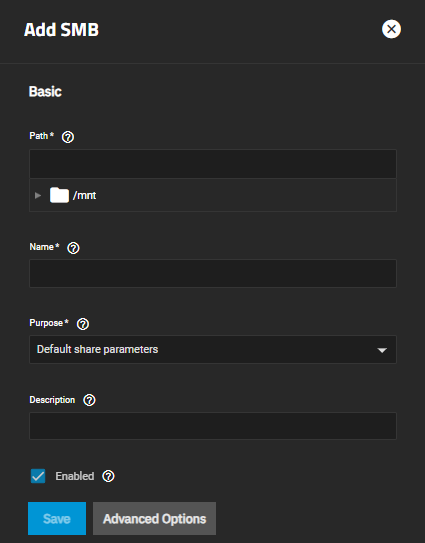
To create the SMB share, go to Shares.
Click on Windows Shares (SMB) to select it and then click Add. The Add SMB configuration screen displays the Basic Options settings.
Enter the SMB share Path and Name.
Enter the path or use the icon to the left of /mnt to locate the dataset you created for the multiprotocol share.
The Name is the SMB share name, which forms part of the share pathname when SMB clients perform an SMB tree connect. Because of how the SMB protocol uses the name, it must be less than or equal to 80 characters. It cannot have invalid characters as specified in Microsoft documentation MS-FSCC section 2.1.6. If you do not enter a name, the share name becomes the last component of the path. If you change the name, follow the naming conventions for:
Select Multi-protocol (NFSv4/SMB) shares from the Purpose dropdown list to apply pre-determined Advanced Options settings for the share.
(Optional) Enter a Description to help explain the share purpose.
Select Enabled to allow sharing of this path when the SMB service is activated. Leave it cleared if you want to disable the share without deleting the configuration.
If needed, use Advanced Options to set up guest access, read only access, to set up allowed and denied hosts. or to optimize the SMB share for Apple OS. See Adding SMB Shares for more information.
Click Save to create the share and add it to the Shares > Windows (SMB) Shares list.
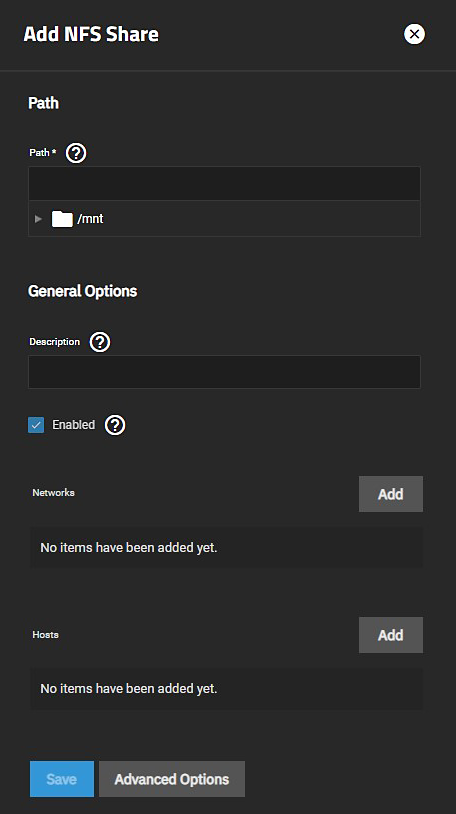
To create the NFS share, go to Shares.
Click on Unix (NFS) Shares to select it and then click Add. The Add NFS Share configuration screen displays the Basic Options settings.
Enter the path or use the icon to the left of /mnt to locate the dataset you created for the multiprotocol share.
Enter text to help identify the share in Description.
If needed, enter allowed networks and hosts.
Enable Kereberos security.
Click Advanced Options.
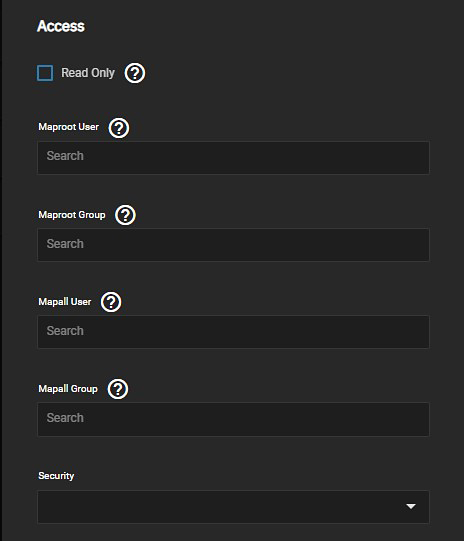
If needed, select Read-Only to prohibit writing to the share.
Select KRB5 from the Security dropdown to enable the Kerberos ticket that generated when you joined Active Directory.
Click Save to create the share.
After you create and configure the shares, connect to your mulitprotocol share using either SMB or NFS protocols from a variety of client operating systems including Windows, Apple, FreeBSD, and Linux/Unix systems. For more information on accessing shares, see Mounting the SMB Share and Connecting to the NFS Share.