TrueNAS Documentation Archive
This content follows the TrueNAS 23.10 (Cobia) releases. Archival documentation is provided for reference only and not actively maintained. Use the Product and Version selectors above to view content specific to different TrueNAS software or major version.
Setting Up a Local Replication Task
9 minute read.
Last Modified 2024-03-19 08:38 EDTA local replication creates a zfs snapshot and saves it to another location on the same TrueNAS SCALE system either using a different pool, or dataset or zvol. This allows users with only one system to take quick data backups or snapshots of their data when they have only one system. In this scenario, create a dataset on the same pool to store the replication snapshots. You can create and use a zvol for this purpose. If configuring local replication on a system with more than one pool, create a dataset to use for the replicated snapshots on one of those pools.
While we recommend regularly scheduled replications to a remote location as the optimal backup scenario, this is useful when no remote backup locations are available, or when a disk is in immediate danger of failure.
Storage space you allocate to a zvol is only used by that volume, it does not get reallocated back to the total storage capacity of the pool or dataset where you create the zvol if it goes unused. Plan your anticipated storage need before you create the zvol to avoid creating a zvol that exceeds your storage needs for this volume. Do not assign capacity that exceeds what is required for SCALE to operate properly. For more information, see SCALE Hardware Guide for CPU, memory and storage capacity information.
With the implementation of rootless login and the admin user, setting up replication tasks as an admin user has a few differences over setting up replication tasks when logged in as root.
The first snapshot taken for a task creates a full file system snapshot, and all subsequent snapshots taken for that task are incremental to capture differences occurring between the full and subsequent incremental snapshots.
Scheduling options allow users to run replication tasks daily, weekly, monthly, or on a custom schedule. Users also have the option to run a scheduled job on demand.
Replication tasks require a periodic snapshot task. The earlier releases of SCALE required creating a periodic snapshot task before the replication task, but SCALE 22.12 and newer automatically creates the snapshot task when a scheduled replication task starts. To start a replication task using the Run Now option on the Replication Task widget or by selecting Run Once in the Replication Task Wizard, create a periodic snapshot task first.
This section provides a simple overview of setting up a replication task regardless of the type of replication, local or remote. It also covers the related steps you should take prior to configuring a replication task.
The replication wizard allows users to create and copy ZFS snapshots to another location on the same system.
If you have an existing replication task, you can select it on the Load Previous Replication Task dropdown list to load the configuration settings for that task into the wizard, and then make change such as assigning it a different destination, schedule, or retention lifetime, etc. Saving changes to the configuration creates a new replication task without altering the task you loaded into the wizard.
Before you begin configuring the replication task, first verify the destination dataset you want to use to store the replication snapshots is free of existing snapshots, or that snapshots with critical data are backed up before you create the task.
To create a replication task:
Create the destination dataset or storage location you want to use to store the replication snapshots. If using another TrueNAS SCALE system, create a dataset in one of your pools.
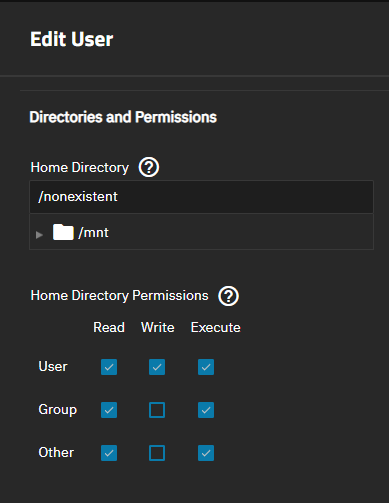
Verify the admin user home directory, auxiliary groups, and sudo setting on both the local and remote destination systems. Local replication does not require an SSH connection so this only applies to replication to another system.
If using a TrueNAS CORE system as the remote server, the remote user is always root.
If using a TrueNAS SCALE system on an earlier release like Angelfish, the remote user is always root.
If using an earlier TrueNAS SCALE Bluefin system (22.12.1) or you installed SCALE as the root user, then created the admin user after initial installation, you must verify the admin user is correctly configured.
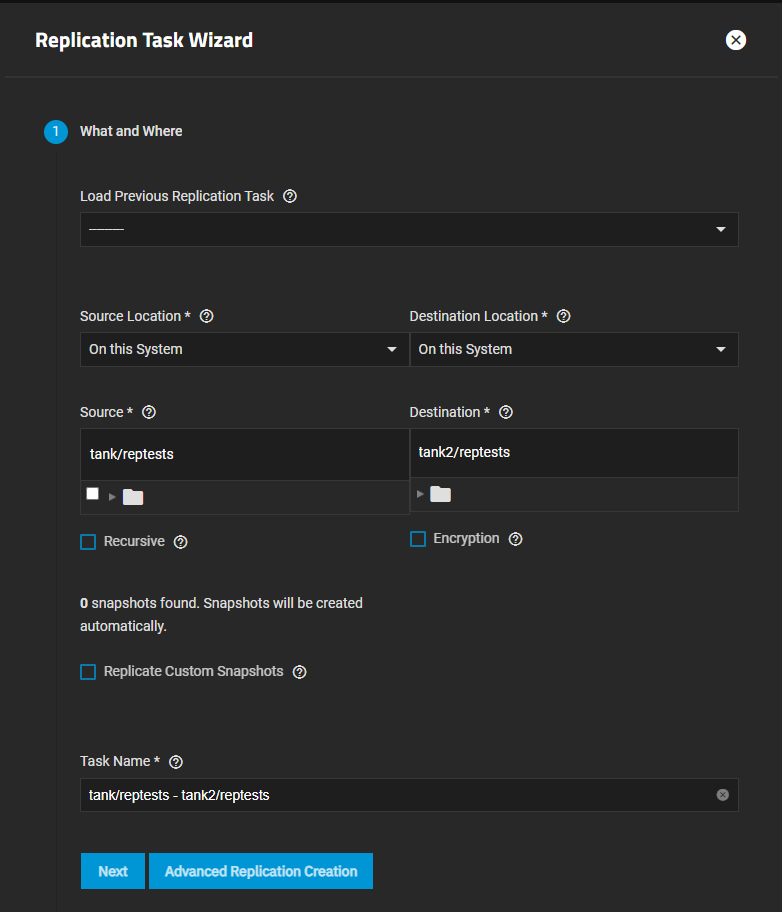
- Go to Data Protection and click Add on the Replication Tasks widget to open the Replication Task Wizard. Configure the following settings:
a. Select On this System on the Source Location dropdown list. Browse to the location of the pool or dataset you want to replicate and select it so it populates Source with the path. Selecting Recursive replicates all snapshots contained within the selected source dataset snapshots.
b. Select On this System on the Destination Location dropdown list. Browse to the location of the pool or dataset you want to use to store replicated snapshots and select to populate Destination with the path.
c. (Optional) Enter a name for the snapshot in Task Name. SCALE populates this field with the default name using the source and destination paths separated by a hyphen, but this default can make locating the snapshot in destination dataset a challenge. To make it easier to find the snapshot, give it name easy for you to identify. For example, a replicated task named dailyfull for a full file system snapshot taken daily.
Click Next to display the scheduling options.
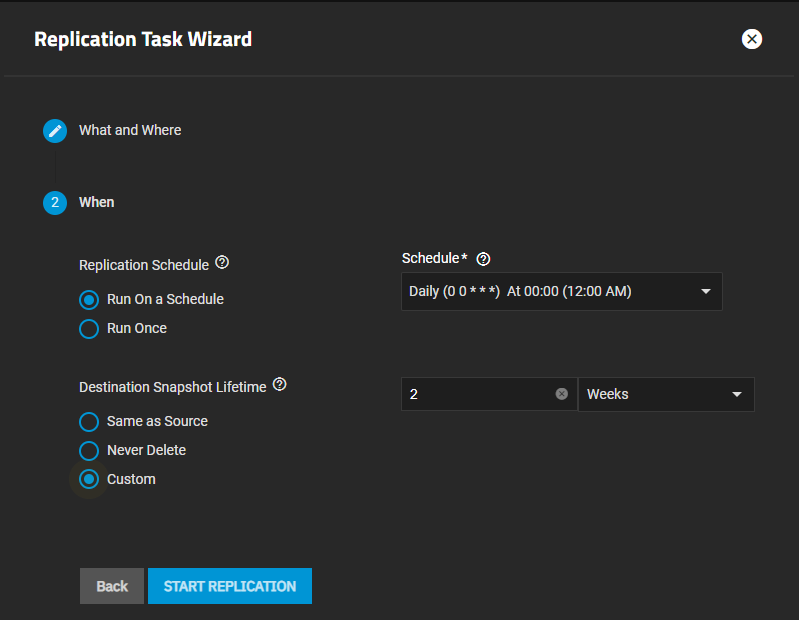
Select the schedule and snapshot retention life time.
a. Select the Replication Schedule radio button you want to use. Select Run Once to set up a replication task you run one time. Select Run On a Schedule then select when from the Schedule dropdown list.
b. Select the Destination Snapshot Lifetime radio button option you want to use. This specifies how long SCALE should store copied snapshots in the destination dataset before SCALE deletes it. Same as Source is selected by default. Select Never Delete to keep all snapshots until you delete them manually. Select Custom to show two additional settings, then enter the number of the duration you select from the dropdown list. For example, 2 Weeks.
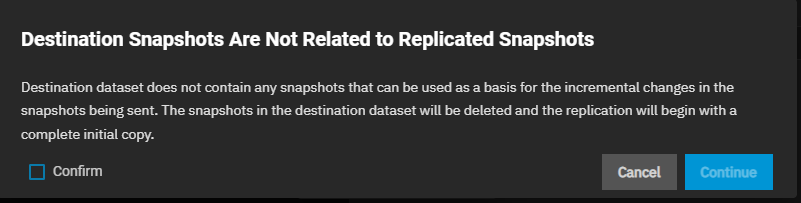
Click START REPLICATION. A dialog displays if this is the first snapshot taken using the destination dataset. If SCALE does not find a replicated snapshot in the destination dataset to use to create an incremental snapshot, it deletes any existing snapshots found and creates a full copy of the day snapshot to use as a basis for the future scheduled incremental snapshots for this schedule task. This operation can delete important data, so ensure you can delete any existing snapshots or back them up in another location.
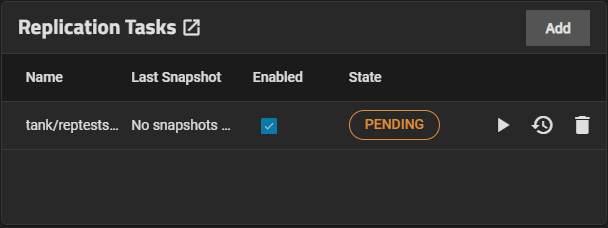
Click Confirm, then Continue to add the task to the Replication Task widget. The newly added task shows the status as PENDING until it runs on the schedule you set.
Select Run Now if you want to run the task immediately.
To see a log for a task, click the task State to open a dialog with the log for that replication task.
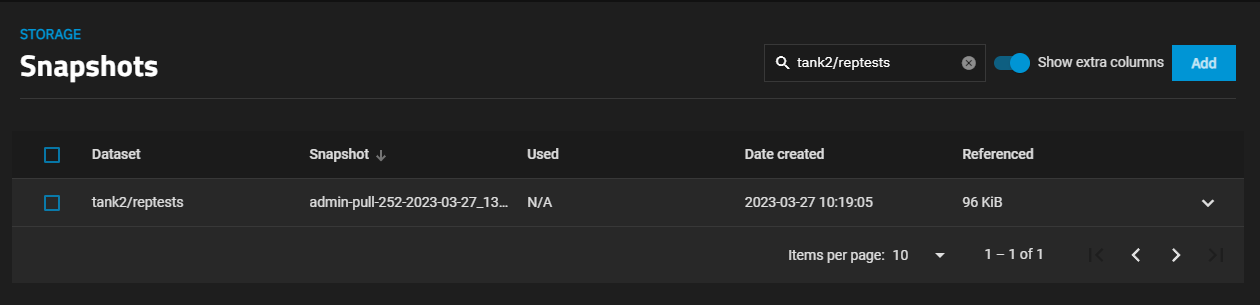
To see the replication snapshots, go to Datasets, select the destination dataset on the tree table, then select Manage Snapshots on the Data Protection widget to see the list of snapshots in that dataset. Click Show extra columns to add more information columns to the table such as the date created which can help you locate a specific snapshot or enter part of or the full the name in the search field to narrow the list of snapshots.
Related Content
- Setting Up Advanced Replication Tasks
- Setting Up an Encrypted Replication Task
- Advanced Settings
- Advanced Settings Screen
- Replication
- Setting Up a Remote Replication Task
- Unlocking a Replication Encrypted Dataset or Zvol
- Adding Periodic Snapshot Tasks
- Periodic Snapshot Tasks Screens