TrueNAS SCALE Documentation Archive
This content follows the TrueNAS SCALE 22.12 (Bluefin) releases. Archival documentation is provided for reference only and not actively maintained.
Use the Product and Version selectors above to view content specific to different TrueNAS software or major versions.
Advanced Settings Screen
10 minute read.
Last Modified 2024-03-19 08:47 EDTThe Advanced settings screen provides configuration options for the console, syslog, cron jobs, init/shutdown scripts, sysctl, storage (system dataset pool), replication, sessions, self-encrypting drives, and isolated GPU device(s).
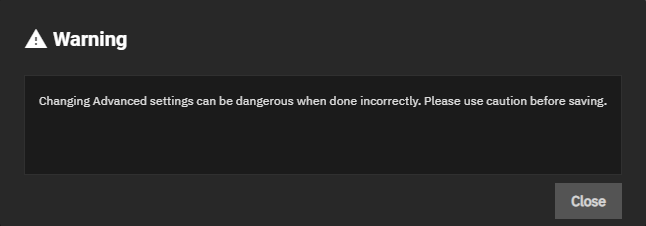
Advanced settings have reasonable defaults in place. A warning message displays for some settings advising of the dangers making changes. Changing advanced settings can be dangerous when done incorrectly. Use caution before saving changes.
Make sure you are comfortable with ZFS, Linux, and system configuration backup and restoration before making any changes.
Save Debug saves a system debug file to the local machine.
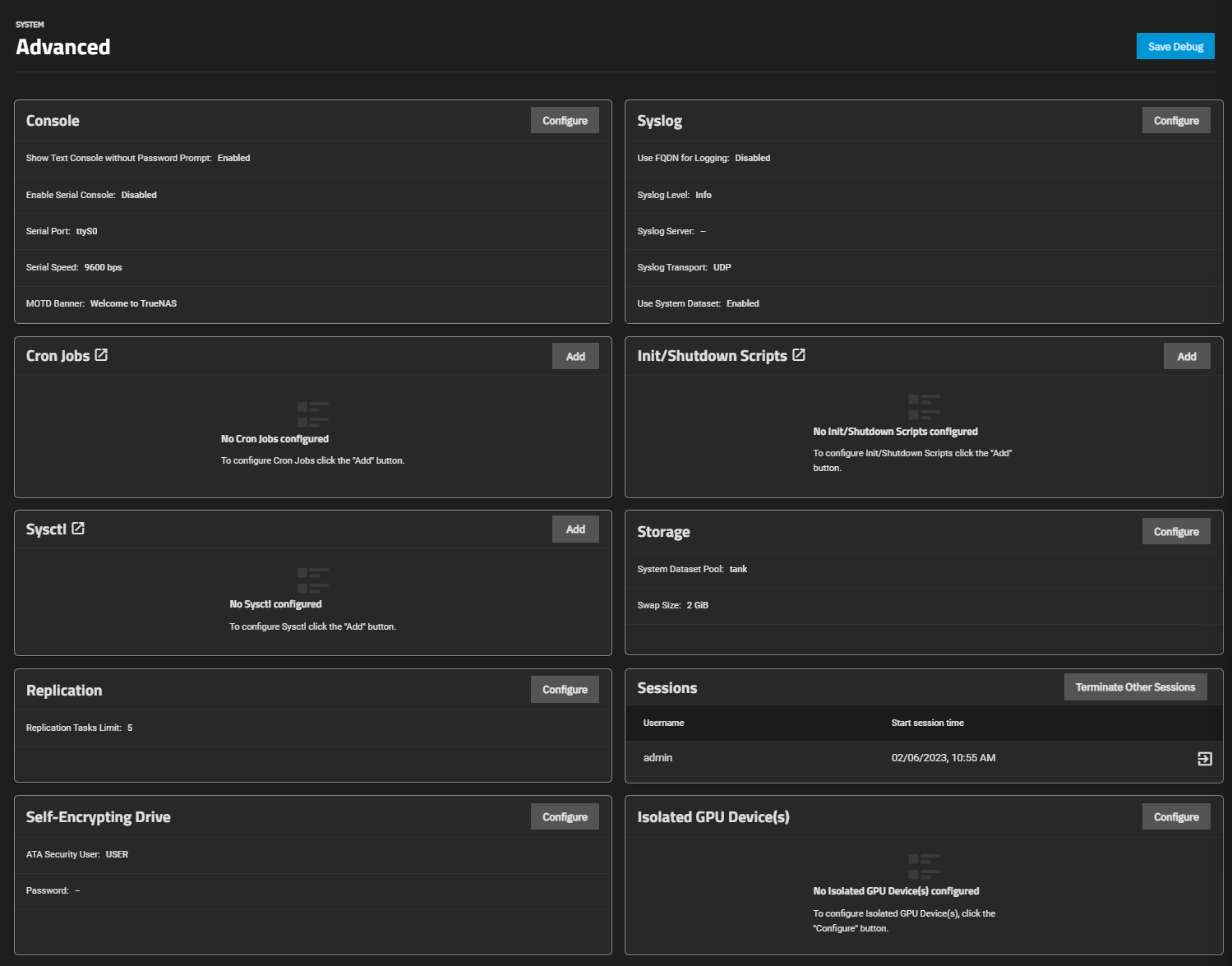
The Console widget on the System Setting > Advanced screen displays current console settings for TrueNAS.
Configure opens the Console configuration screen.
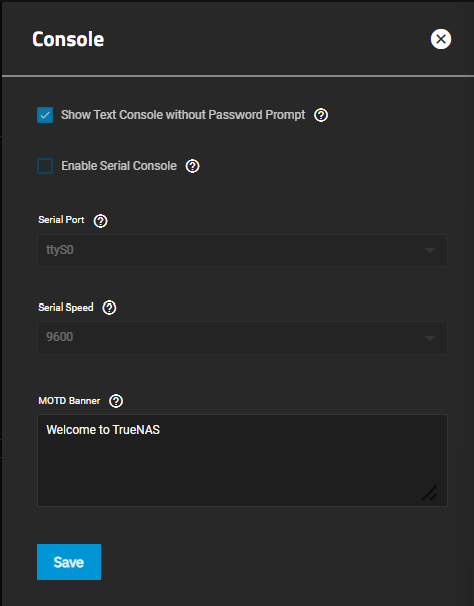
Console settings configure how the Console setup menu displays, the serial port it uses and the port speed, and the banner users see when accessing it.
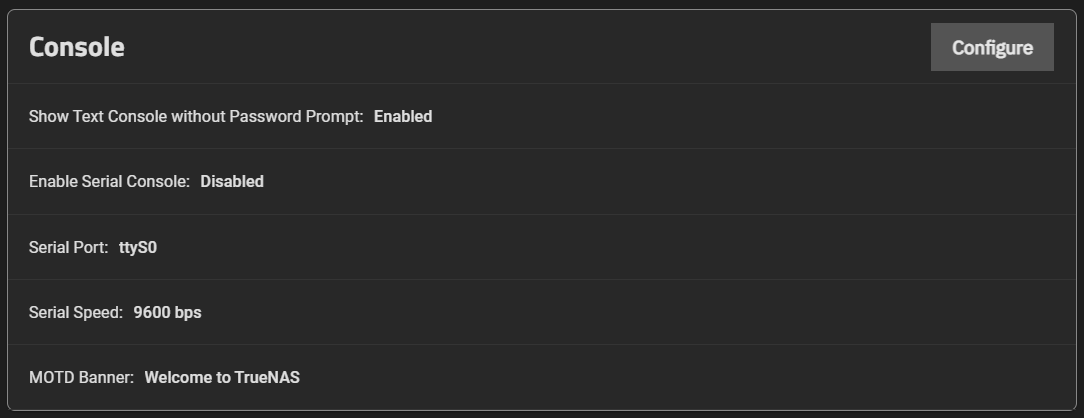
The Syslog widget displays the existing system logging settings that specify how and when the system sends log messages to the syslog server.
Configure opens the Syslog configuration screen.
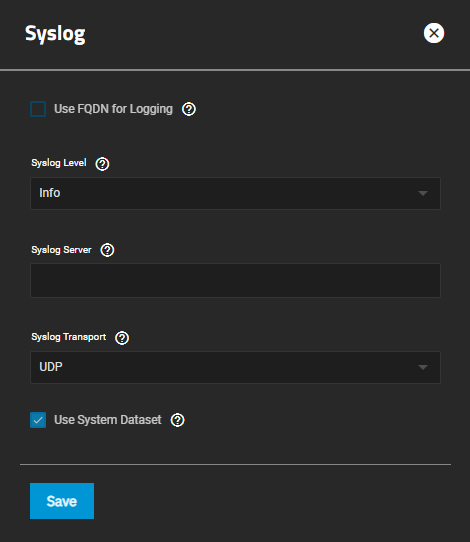
The Syslog settings specify the logging level the system uses to record system events. It also lists the syslog server DNS hostname or IP, the transport protocol it uses, the certificate and certificate authority (CA) for that server (if using TLS), and, finally, if it uses the system dataset to store logs.
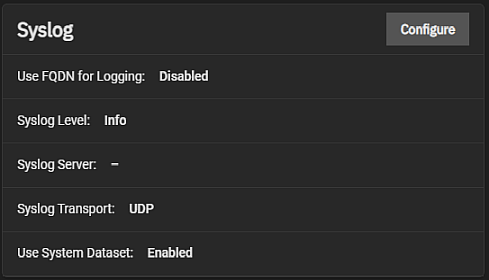
The Cron Jobs widget displays No Cron Jobs configured until you add a cron job, then it shows the information on cron job(s) configured on the system.
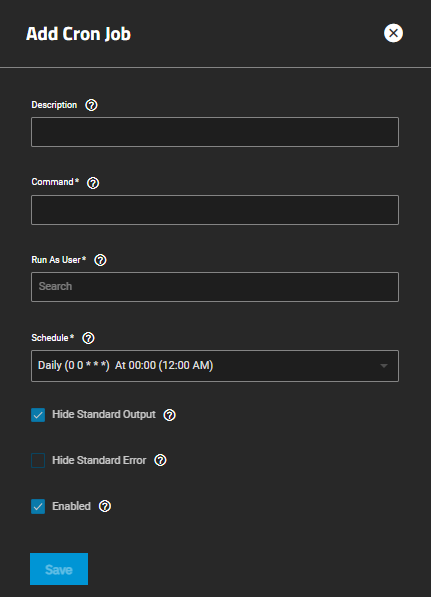
Add opens the **Add Cron Job configuration screen. Click on any job listed in the widget to open the **Edit Cron Jobs configuration screen populated with the settings for that cron job.
The Add Cron Job and Edit Cron Job configuration screens display the same settings. Cron Jobs lets users configure jobs that run specific commands or scripts on a regular schedule using cron(8). Cron Jobs help users run repetitive tasks.
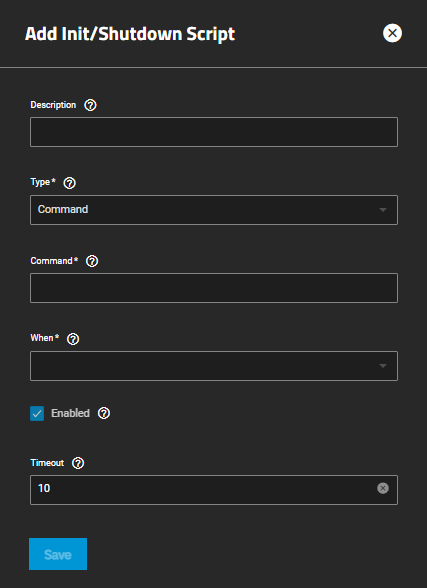
The Init/Shutdown Scripts widget displays No Init/Shutdown Scripts configured until you add either a command or script, then the widget lists the scrips configured on the system.
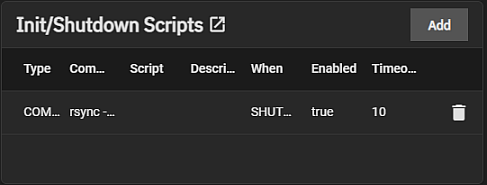
Add opens the Add Init/Shutdown Script configuration screen. Any script listed is a link that opens the Edit Init/Shutdown Script configuration screen populated with the settings for that script.
Init/Shutdown Scripts lets users schedule commands or scripts to run at system startup or shutdown.
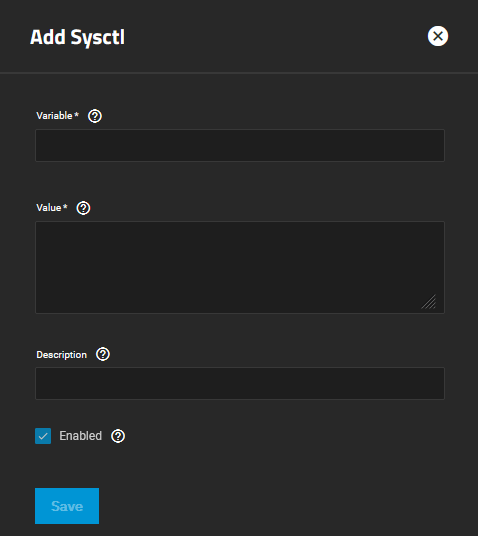
The Sysctl widget displays either No Sysctl configured or the existing sysctl settings on the system.
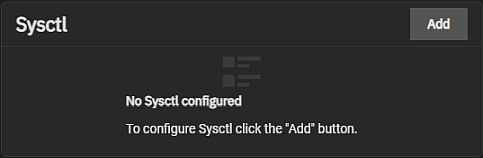
Add to add a tunable that configures a kernel module parameter at runtime.
The Add Sysctl or Edit Sysctl configuration screen settings let users set up tunables that configure kernel parameters at runtime.
Storage widget displays the pool configured as the system dataset pool and allows users to select the storage pool they want to hold the system dataset. The system dataset stores core files for debugging and keys for encrypted pools. It also stores Samba4 metadata, such as the user and group cache and share-level permissions.
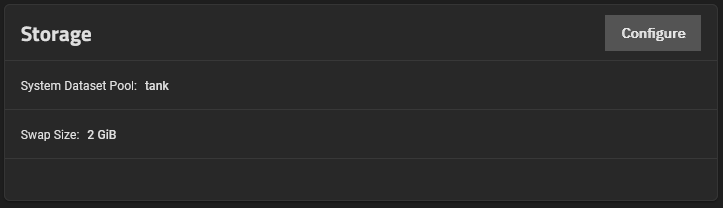
Configure opens the Storage Settings configuration screen.
If the system has one pool, TrueNAS configures that pool as the system dataset pool. If your system has more than one pool, you can set the system dataset pool using the Select Pool dropdown. Users can move the system dataset to an unencrypted pool, or an encrypted pool without passphrases.
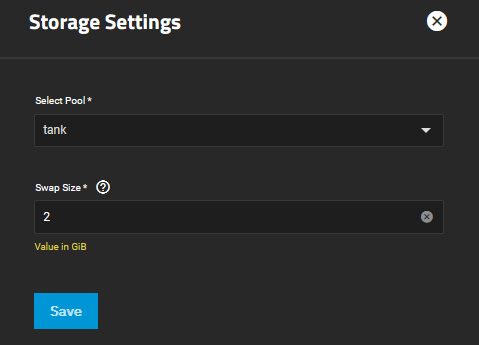
Users can move the system dataset to a key-encrypted pool, but cannot change the pool encryption type afterward. If the encrypted pool already has a passphrase set, you cannot move the system dataset to that pool.
Swap Size lets users enter an amount (in GiB) of hard disk space to use as a substitute for RAM when the system fully utilizes the actual RAM.
By default, the system creates all data disks with the specified swap amount. Changing the value does not affect the amount of swap on existing disks, only disks added after the change. Swap size does not affect log or cache devices.
The Replication widget displays the number of replication tasks that can execute simultaneously configured on the system. It allows users to adjust the maximum number of replication tasks the system can perform simultaneously.
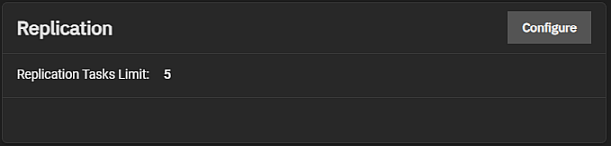
Click Configure to open the Replication configuration screen.
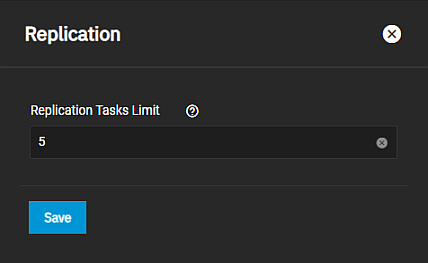
Enter a number for the maximum number of simultaneous replication tasks you want to allow the system to process and click Save.
The Sessions widget displays all active sessions in the web UI, along with the user who initiated the session and what time it started.
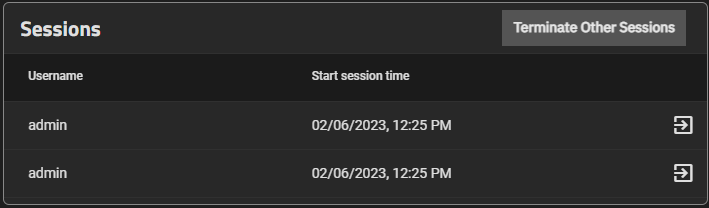
The Terminate Other Sessions button ends all sessions except for the one you are currently using. You can also end individual sessions by clicking the button next to that session. You must check a confirmation box before the system allows you to end sessions.
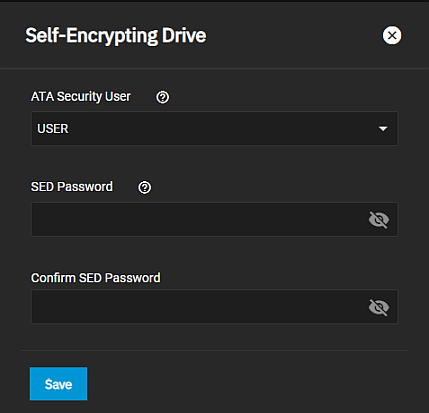
The Self-Encrypting Drive (SED) widget displays the system ATA security user and password.
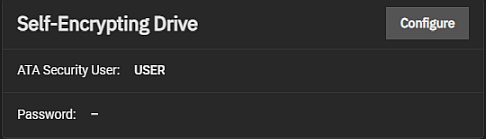
Configure opens the Self-Encrypting Drive configuration screen.
The Self-Encrypting Drive configuration screen allows users to set the ATA security user and create a SED global password.
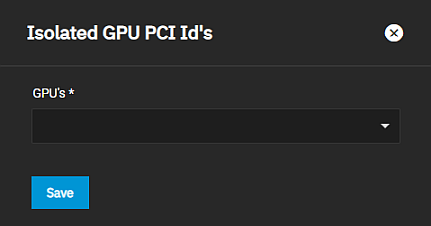
The Isolated GPU Device(s) widget displays any graphics processing unit (GPU) device(s) configured on your system.
Configure opens the Isolate GPU PCI’s ID screen, which allows users to isolate additional GPU devices for GPU passthrough.
The Isolate GPU PCI’s ID configuration screen allows you to add GPU devices to your system.