TrueNAS SCALE Documentation Archive
This content follows the TrueNAS SCALE 22.12 (Bluefin) releases. Archival documentation is provided for reference only and not actively maintained.
Use the Product and Version selectors above to view content specific to different TrueNAS software or major versions.
Managing Snapshots
5 minute read.
Last Modified 2024-03-19 08:47 EDTFile Explorer limits the number of snapshots Windows presents to users. If TrueNAS responds with more than the File Explorer limit, File Explorer shows no available snapshots. TrueNAS displays a dialog stating the dataset snapshot count has more snapshots than recommended, and states performance or functionality might degrade.
There are two ways to view the list of snapshots:
- Go to Datasets > Data Protection widget > Manage Snapshots link to open the Snapshots screen,
- Go to Data Protection, locate the Periodic Snapshot Tasks widget, then click the Snapshots button in the lower right hand corner of the widget.
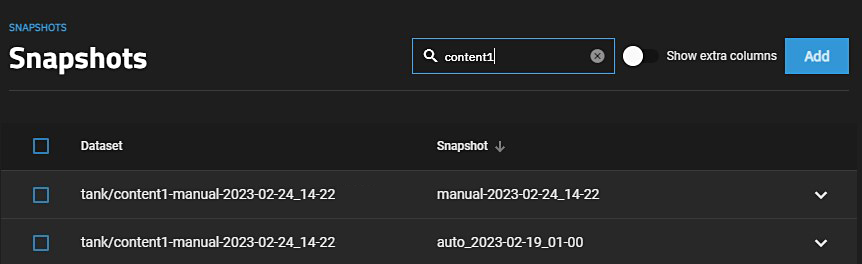
The Snapshots screen displays a list of snapshots on the system. Use the search bar at top to narrow the selection, clear the search bar to list all snapshots.
Click to view snapshot options.
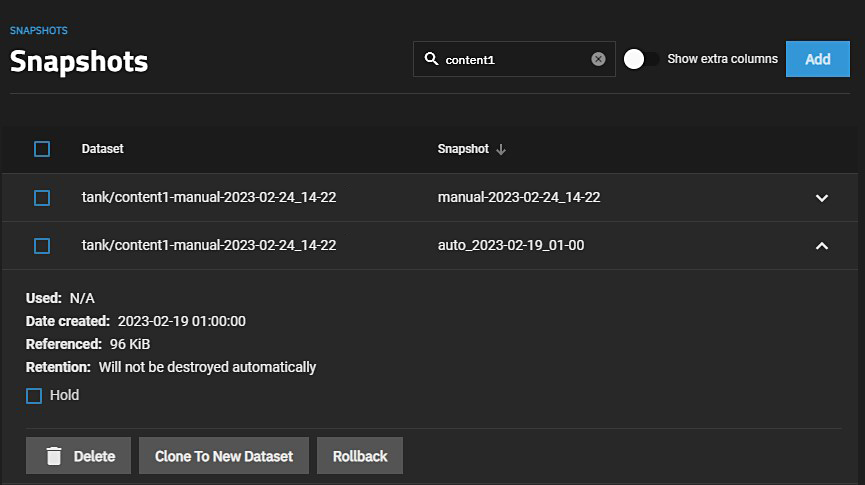
The Clone to New Dataset button creates a clone of the snapshot. The clone appears directly beneath the parent dataset in the dataset tree table on the Datasets screen. Clicking the Clone to New Dataset button opens a clone confirmation dialog.
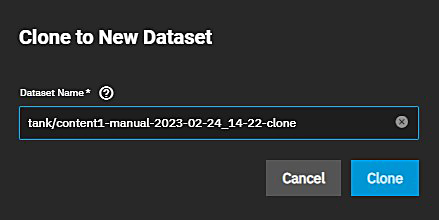
Click Clone to confirm.
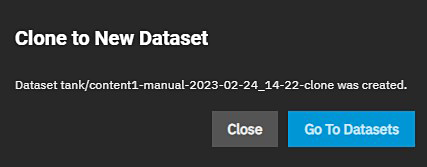
The Go to Datasets button opens the Datasets screen.
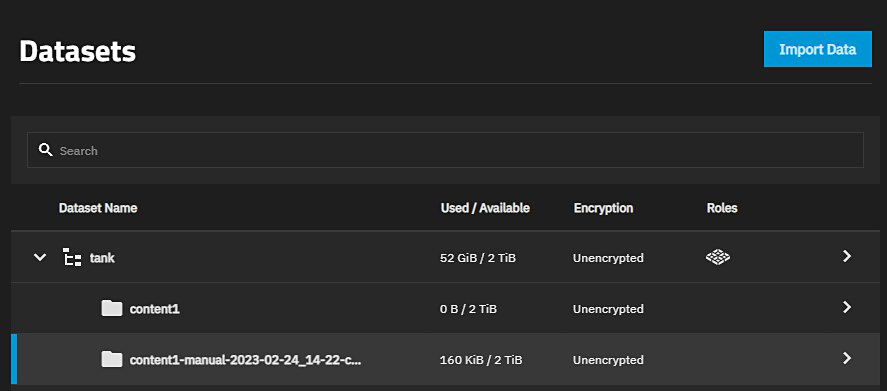
Clicking on the clone name in the dataset listing populates the Dataset Details widget. The Promote button is visible.
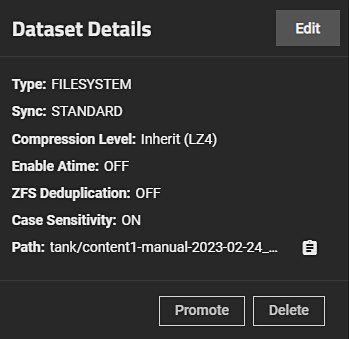
After clicking the Promote button, the dataset clone is promoted and this button no longer appears.
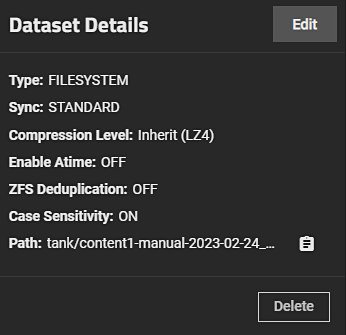
Promote now displays on the Dataset Details widget when you select the demoted parent dataset.
See zfs-promote.8 for more information.
The Delete option destroys the snapshot. You must delete child clones before you can delete their parent snapshot. While creating a snapshot is instantaneous, deleting one is I/O intensive and can take a long time, especially when deduplication is enabled.
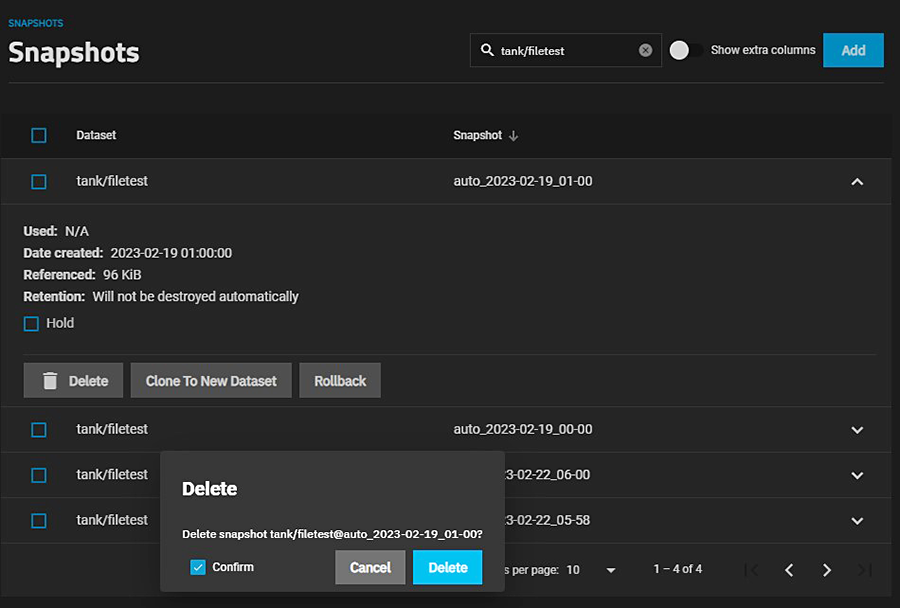
Click the Delete button. A confirmation dialog displays. Select Confirm to activate the Delete button.
To delete multiple snapshots, select the left column box for each snapshot to include. Click the delete Delete button that displays.
To search through the snapshots list by name, type a matching criteria into the search Filter Snapshots text field. The list now displays only the snapshot names that match the filter text.
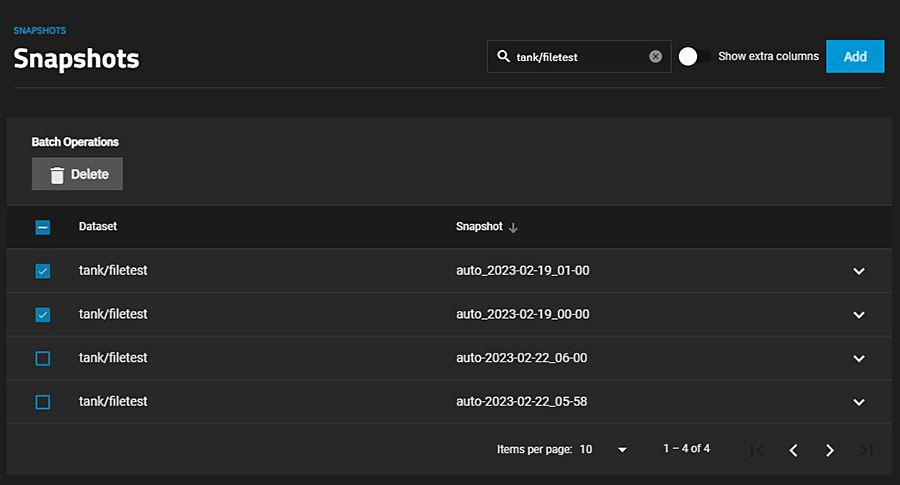
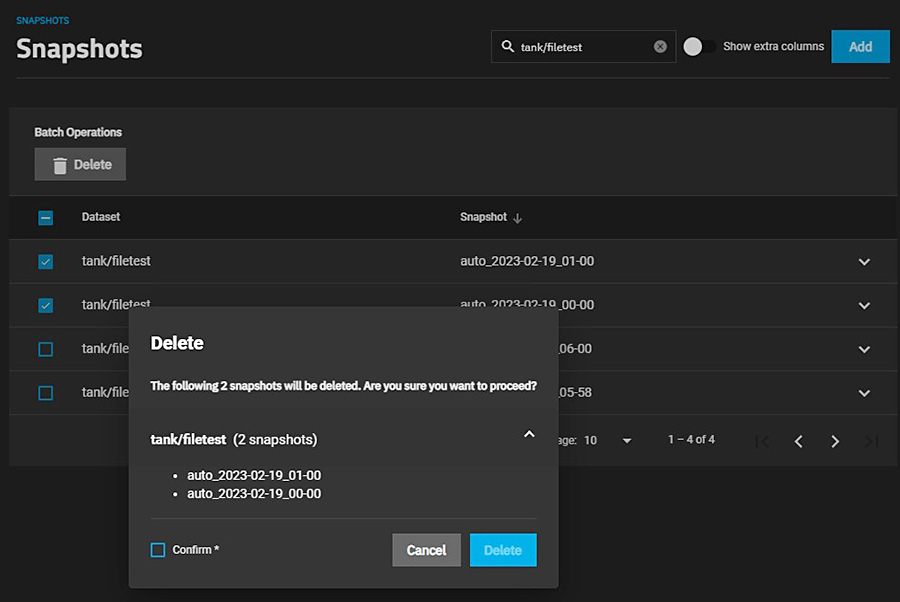
Confirm activates the Delete button. If the snapshot has the Hold options selected, an error displays to prevent you from deleting that snapshot.
The Rollback option reverts the dataset back to the point in time saved by the snapshot.
Replications use the existing snapshot when doing an incremental backup, and rolling back can put the snapshots out-of-order. To restore the data within a snapshot:Rollback is a dangerous operation that causes any configured replication tasks to fail.
- Clone the desired snapshot.
- Share the clone with the share type or service running on the TrueNAS system.
- Allow users to recover their needed data.
- Delete the clone from Datasets.
This approach does not destroy any on-disk data or impact replication.
TrueNAS asks for confirmation before rolling back to the chosen snapshot state. Select the radio button for how you want the rollback to operate.
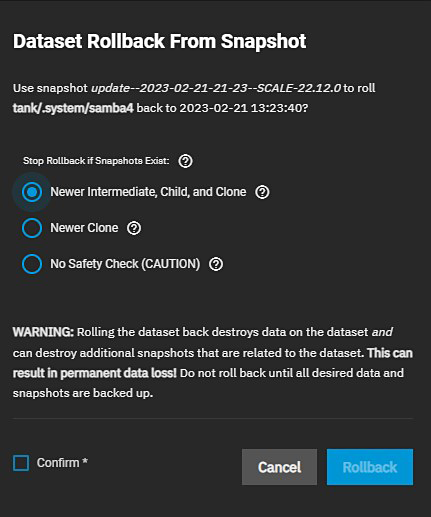
Click Confirm to activate the Rollback button.
Browsing a snapshot collection is an advanced capability that requires ZFS and command-line experience.
All dataset snapshots are accessible as an ordinary hierarchical file system, accessed from a hidden
A snapshot and any files it contains are not accessible or searchable if the snapshot mount path is longer than 88 characters. The data within the snapshot is safe but to make the snapshot accessible again shorten the mount path.
A user with permission to access the hidden file can view and explore all snapshots for a dataset from the Shell or the Shares screen using services like SMB, NFS, and SFTP.
In summary, the main required changes to settings are:
- In dataset properties, change the ZFS properties to enable snapshot visibility.
- In the Samba auxiliary settings, change the
veto filescommand to not hide the.zfs , and add the settingzfsacl:expose_snapdir=true.
The effect is that any user who can access the dataset contents can view the list of snapshots by going to the dataset
When creating a snapshot, permissions or ACLs set on files within that snapshot might limit access to the files.
Snapshots are read-only, so users do not have permission to modify a snapshot or its files, even if they had write permissions when creating the snapshot.
The zfs diff ZFS command, which can run in the Shell, lists all changed files between any two snapshot versions within a dataset, or between any snapshot and the current data.

